Python Shelve Module
The shelve module allows you to save a class or a structured object to an external file, separate from your program.
Why use it? Once you've created the object, you can reload it at any time, whether in the same program or in different ones.
A Practical Example
To show how the shelve module works, let's go through a practical example.
We'll create two separate programs (A and B).
- Program A saves a structured object.
- Program B reads the object.
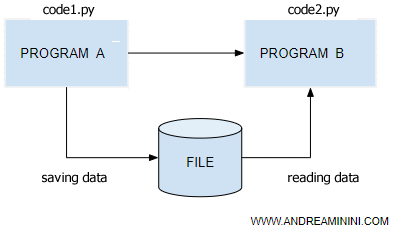
How to Create and Save an Object
Program A creates a class called Rubrica and adds an object to it.
- import shelve
- db = shelve.open('nome')
- class Rubrica:
- def __init__(self, nome):
- self.nome = nome
- var = Rubrica('Minini')
- db['Andrea'] = var
- db.close()
The class and its data are saved to an external file (nomefile) using the shelve module.
How to Read the Object
Program B then reads the object (nomefile) and retrieves the data stored in it.
- import shelve
- class Rubrica:
- def __init__(self, nome):
- self.nome = nome
- db = shelve.open('db')
- var = db['Andrea']
- print(var.nome)
The output of the program is:
Minini
With this module, you can easily transfer a class and its data from one program to another using a binary file.
And that’s it!
