DIR Command in Python
In Python, the dir command lists an object's attributes.
Syntax of the dir Command
dir(object_name)
The dir command is particularly useful in Python's interactive mode, which is accessed via the command line (shell).
How the Python dir Command Works
Open the Python shell and initialize a variable named name.
Assign it the alphanumeric value "Andrea Minini".
Press Enter.
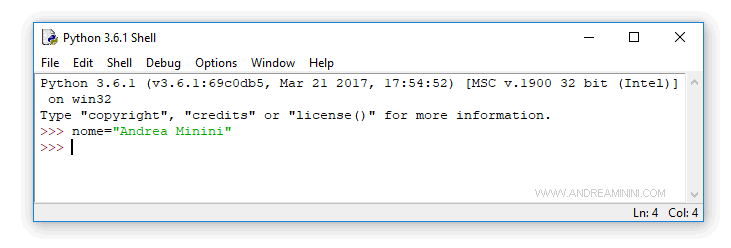
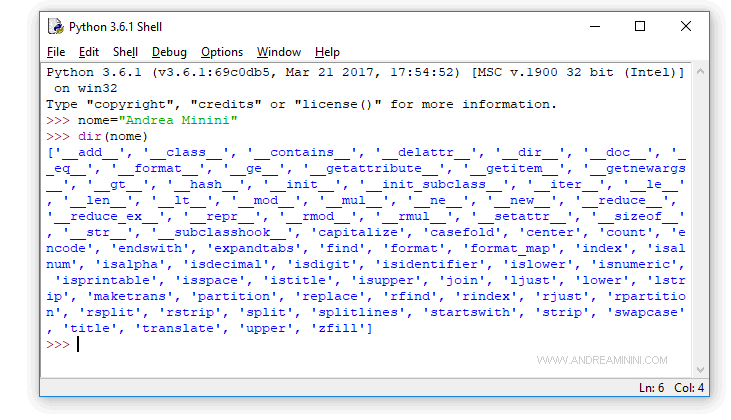
To see the attributes of the name variable, type dir(name) at the prompt and press Enter.
The interpreter will display a list of attributes for the variable name.
What is the dir Command Used For?
Knowing the list of attributes is very helpful for debugging.
For instance, the __class__ attribute of an object reveals its type (string, numeric, boolean, etc.).
name="Andrea Minini"
name.__class__
<class 'str'>
Additionally, with the dir function, you can view all the functions available in a library.
import math
dir(math)
The output shows a list of functions in the math library.
['__doc__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'acos', 'acosh', 'asin', 'asinh', 'atan', 'atan2', 'atanh', 'ceil', 'copysign', 'cos', 'cosh', 'degrees', 'e', 'erf', 'erfc', 'exp', 'expm1', 'fabs', 'factorial', 'floor', 'fmod', 'frexp', 'fsum', 'gamma', 'gcd', 'hypot', 'inf', 'isclose', 'isfinite', 'isinf', 'isnan', 'ldexp', 'lgamma', 'log', 'log10', 'log1p', 'log2', 'modf', 'nan', 'pi', 'pow', 'radians', 'sin', 'sinh', 'sqrt', 'tan', 'tanh', 'tau', 'trunc']
And so on.
