Calculating the Dot Product in GeoGebra
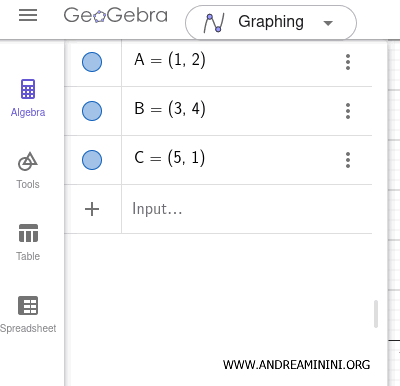
To compute the dot product in GeoGebra, follow these steps: First, define the points that determine the vectors. For example, you can create three points: A = (1,2), B = (3,4), and C = (5,1).
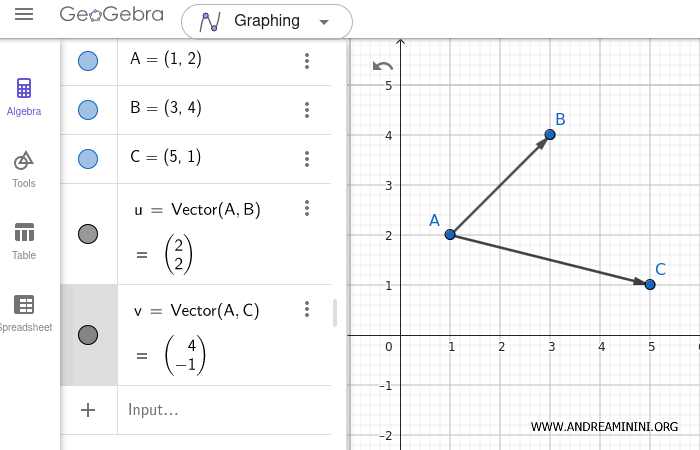
Next, define the vectors.
In the input bar, type u = Vector(A, B) to create the first vector and v = Vector(A, C) for the second.
Note: If the vectors originate from (0,0), you can enter their coordinates directly: a = (2,2) and b = (4,-1).
Now, calculate the dot product of the two vectors.
In the input bar, enter dot(u, v) (in the English version of GeoGebra).
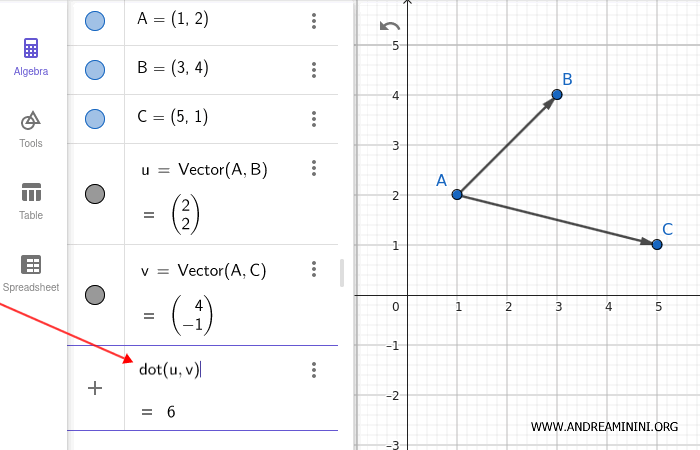
GeoGebra instantly computes and displays the numerical value of the dot product.
In this case, the result is 6.
For additional insight, use the function angle(v, u) to determine the angle between the two vectors.
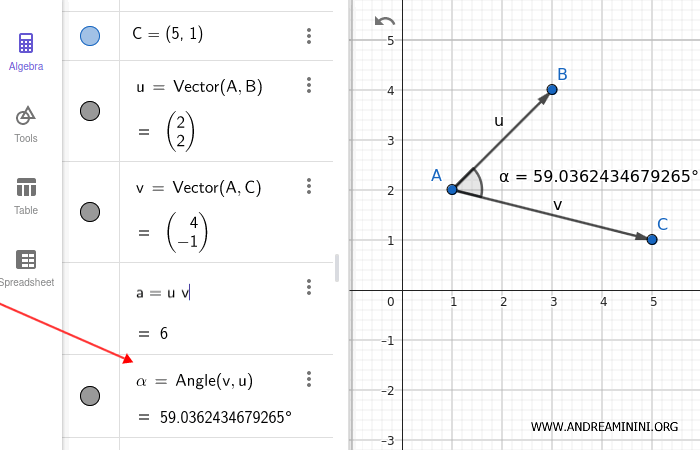
The two vectors form an acute angle of approximately 59°.
Interpreting the result
The dot product provides useful information about the relationship between vectors:
- If the dot product is positive, the vectors form an acute angle.
- If it equals zero, the vectors are perpendicular (forming a right angle).
- If it's negative, the vectors form an obtuse angle.
To learn more about the dot product in mathematics, click here.
And so on.
