Super Function in Python Classes
The super function in Python is a powerful tool that allows you to extend or modify a method from a parent class within a child class that inherits it.
Syntax
super(child_class, method_name)
This function takes two arguments:
- The name of the child class (subclass) that inherits the method from the parent (or base) class.
- The name of the method you want to extend in the child class.
A Practical Example
Let's start by creating a base class, Class1:
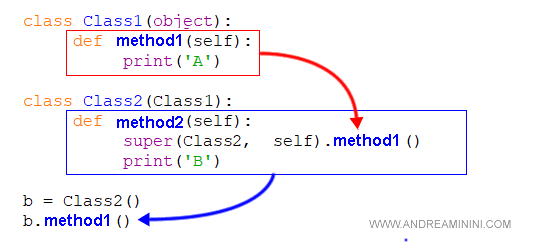
class Class1(object):
def method1(self):
print('A')
Next, we'll create a child class, Class2, that inherits from Class1:
class Class2(Class1):
def method2(self):
super(Class2, self).method1()
print('B')
In this child class, I've defined a new method called method2.
Within this method, I use the super() function to call method1() from the base class, Class1.
After that, the method prints the character "B".
Why Use It?
To see this in action, let's assign an instance of Class2 to a variable, b.
Then, we'll call method2:
b = Class2()
b.method2()
The output will be:
A
B
Here’s what happens: method2 in Class2 first calls method1 from Class1, which prints "A".
Then, it continues to print "B" from method2 in Class2.
In conclusion, the super function effectively extends the behavior of method1() in the child class.
