Linear Equations
An equation is called linear if it can be expressed as a polynomial of degree 1 equal to 0.
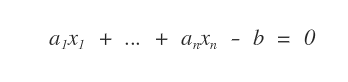
Definition of a Linear Equation
If p(x1, ..., xn) is a degree 1 polynomial with n unknowns x1, ...,xn
a1x1 + ... + anxn -b
where n is an integer belonging to the set of integers Z and is greater than or equal to 1
n ∈ Z ≥ 1
and both the coefficients a1,...,an and the constant term b are real numbers,
then
a1x1 + ... + anxn -b = 0
is a linear equation with n unknowns.
Note: The simplest case is a linear equation with one unknown a1x1 -b = 0 or more simply a1x1 = b.
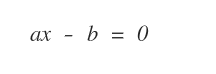
Solving the linear equation
Given a linear equation with n unknowns
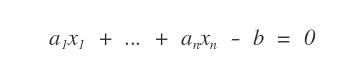
its solution is an ordered n-tuple of real numbers ( s1,..., sn )
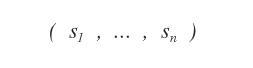
which, when substituted in place of the unknowns ( x1, ..., xn ), make the equation true.
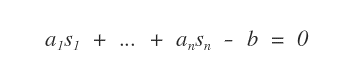
Examples of Linear Equations
The following are examples of linear equations.
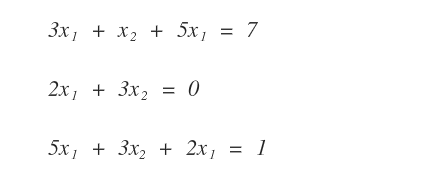
How do we recognize non-linear equations?
An algebraic polynomial equation might not be linear for several reasons.
- If the polynomial is of a degree higher than the first.
- If the equation is not polynomial (for example, if it's transcendental).
Examples of Non-Linear Equations: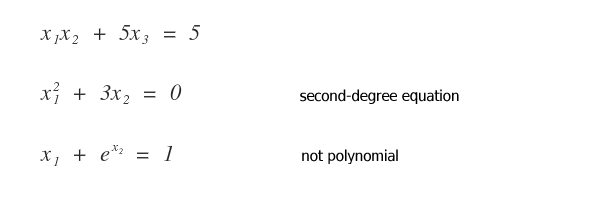
Geometric Representation
A linear equation is represented in an N-dimensional space, equal to the number of unknowns.
Example of a Linear Equation with Two Unknowns
The following linear equation has two unknown variables (x1,x2)
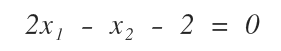
and can be graphically represented by a line on a Cartesian plane.
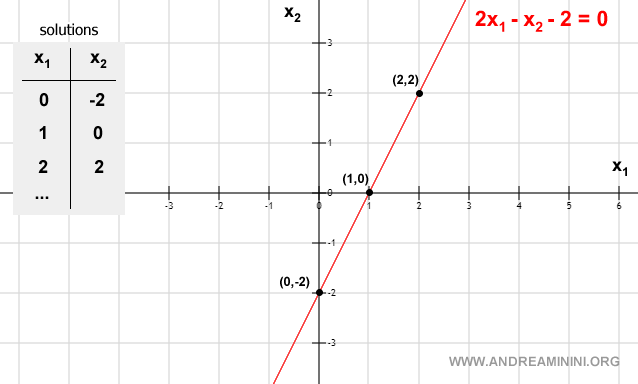
The coordinates (x1,x2) of points on the line identify the ordered pairs of real numbers that are the possible solutions of the linear equation.
The solutions of the linear equation are infinite
The set of possible solutions of the linear equation is infinite, just like the points on the line.
