Difference Quotient of a Function
Definition of the Difference Quotient
The difference quotient of a function is defined as: $$ \frac{f(x + h) - f(x)}{h} $$
The value h represents the increment of the independent variable.
Explanation
Consider a function f(x) defined on an interval (a, b).
$$ f(x) $$
To help visualize the concept, let’s plot the function f(x) on the Cartesian plane.
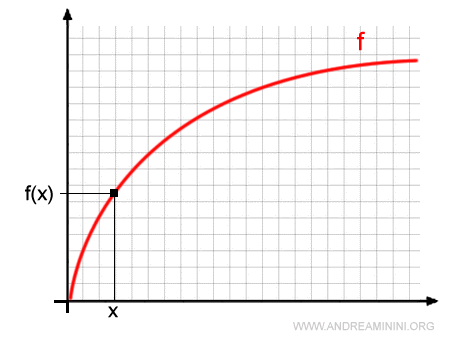
Now, let’s choose an arbitrary value h within the interval (a, b) as an increment of the independent variable x.
When we apply this increment, the function f(x) takes on a new value:
$$ f(x + h) $$
We can illustrate this change on the Cartesian plane:
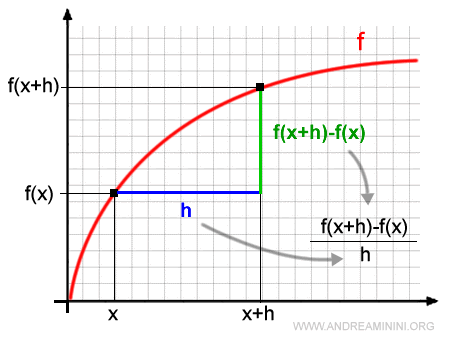
The change in the dependent variable - that is, the change in the function’s value - is given by:
$$ f(x + h) - f(x) $$
The ratio of the change in the dependent variable to the change in the independent variable is called the difference quotient.
$$ \frac{f(x + h) - f(x)}{h} $$
Note. The difference quotient of the function f(x) is defined for any value of h within the interval (a, b), except when h = 0. If h equals zero, the denominator becomes zero, resulting in division by zero, which is mathematically undefined.
