Vector Projection
Understanding Vector Projection
Given a vector and a line, the projection of the vector is achieved by drawing a perpendicular from the line through the end point of the vector.
This perpendicular should be drawn from both the tip and the tail of the vector.
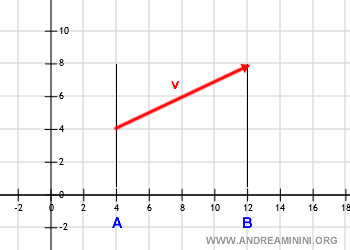
By doing this, the vector's endpoints are projected onto the line at points A and B.
For continuity, all intermediate points between these two are also projections of the vector.
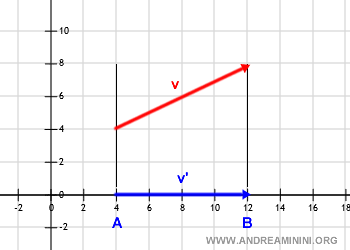
This process results in an orthogonal projection of the vector onto a line.
In this instance, it is the x-axis of the Cartesian plane.
