Deep Learning
Deep Learning, a subset of machine learning, focuses on automatic learning through the use of multi-layered neural networks and recursive neural networks. This field is also known by its abbreviation, DL.
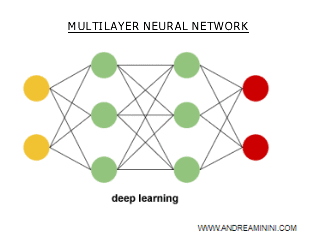
The multiple layers of a neural network consist of cascading non-linear units tasked with extracting information to construct classification models.
This approach to learning is also referred to as non-linear learning.
Note: In Deep Learning, high-level concepts are defined by lower levels.
Like other machine learning techniques, deep learning can be implemented with both supervised and unsupervised algorithms.
The Difference Between Deep Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a broad field in computer engineering encompassing many disciplines, including deep learning.
Example: Artificial Intelligence includes fields like operations research, knowledge representation, logic, machine learning, etc.
AI sometimes overlaps with other areas of knowledge, such as philosophy, neuroscience, and cognitive psychology.
The Difference Between Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Deep learning is a branch of machine learning (ML) that relies on deep neural networks (multilayer neural networks).
Machine learning encompasses a wide range of algorithms and learning methods beyond deep learning.
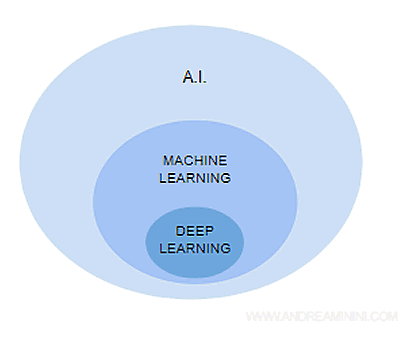
Note: Machine learning is a discipline within Artificial Intelligence. Thus, Artificial Intelligence (AI) includes machine learning (ML), which in turn encompasses deep learning (DL).
The History of Deep Learning
The term 'deep learning' was coined in 2006, but its history dates back 60 years.
Deep learning's history is divided into three historical periods:
- Cybernetics (1950s-60s): This era saw the development of early linear models like the Perceptron and Adaline, introducing the concept of the artificial neuron. These are the cornerstones of deep learning.
- Connectionism (1980s-90s): The 1980s reignited interest in neural networks through connectionist studies in cognitive sciences. This period saw the development of early neural networks with backpropagation and LSTM networks. The models were still inspired by neuroscience and symbolic reasoning.
- Deep Learning (2006-present): This phase began with Hinton's deep belief network model and continues to the present day. The new models, built with multilayer neural networks and numerous hidden layers, are significantly more powerful than their predecessors and are no longer primarily inspired by neuroscience.
