Statistical Population
The population (also referred to as the collective or statistical universe) is a set of statistical units that share certain characteristics, which we aim to study through a statistical survey.
This is the group from which information is gathered.
The statistical units within the population are the individual elements (or objects) of the group, each associated with one or more characteristics (or attributes).
Example: The students in a school form a statistical population. Each student represents a statistical unit. The characteristics of these units include age, gender, nationality, height, weight, the class they attend, and so on. The characteristic of age is expressed through categories that represent age ranges (0-9, 10-14, 15-19 years).
A statistical survey can be conducted on all the units within the population, or just on a subset, known as a sample.
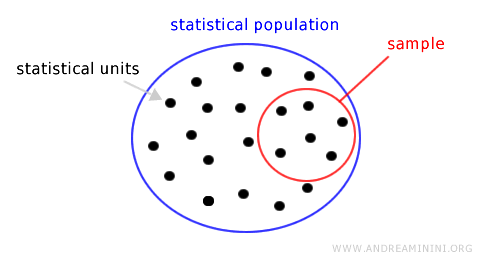
Once results are obtained from the sample analysis, they are generalized to represent the entire population.
Example: In Italy, about 50 million citizens are eligible to vote. Election polls are conducted by analyzing the voting intentions of a sample of just a few thousand citizens.
A sample survey is effective if the sample is representative of the population, meaning it accurately reflects the characteristics of the population on a smaller scale.
To select a representative sample, various selection criteria can be used.
However, finding a truly representative sample can be challenging, and often a random sample is used.
