Trinomial Inequality
A trinomial inequality is an inequality that can be expressed in the form $$ ax^{2n}+bx^n + c > 0 $$ or $$ ax^{2n}+bx^n + c < 0 $$ where a≠0 and n is a positive integer.
To solve a trinomial inequality, an auxiliary variable t is introduced.
$$ t = x^n $$
The inequality can then be rewritten in terms of t and handled as a quadratic inequality.
$$ at^{2}+bt + c > 0 $$
After determining the solution in the auxiliary variable t, the result is converted back to the original variable x.
Note. If n=2, the trinomial inequality reduces to a biquadratic inequality and is solved using the same approach. For example $$ ax^{2\cdot 2}+bx^2 + c > 0 $$ $$ ax^{4}+bx^2 + c > 0 $$
A practical example
Consider the inequality
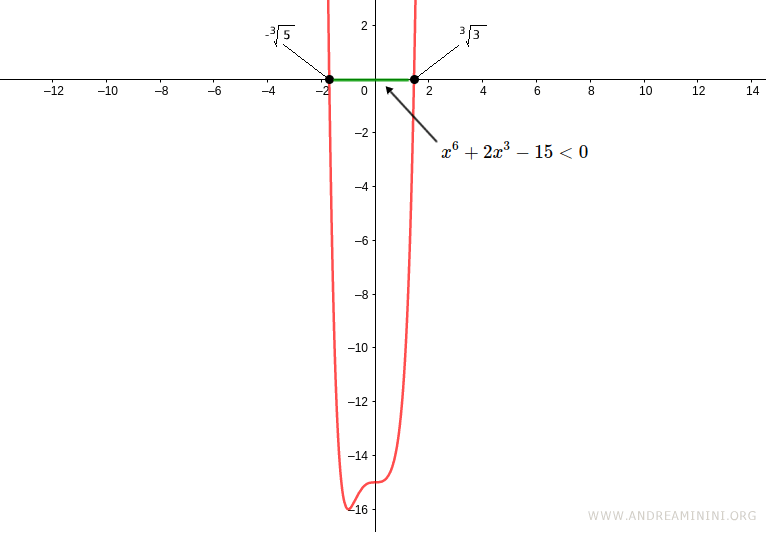
$$ x^6 + 2x^3 -15 < 0 $$
This is a trinomial inequality.
Introduce the auxiliary variable t = x3.
$$ t^2 + 2t -15 < 0 $$
The problem is now reduced to solving a quadratic inequality.
The equation associated with this inequality is
$$ t^2 + 2t -15 = 0 $$
This equation corresponds to a parabola that opens upward, since the coefficient of t2 is positive.
Next, determine whether the associated equation has any real roots.
$$ t = \frac{-2 \pm \sqrt{4-4(1)(-15)}}{2}$$
$$ t = \frac{-2 \pm \sqrt{4+60}}{2}$$
$$ t = \frac{-2 \pm \sqrt{64}}{2}$$
$$ t = \frac{-2 \pm 8}{2} = \begin{cases} t_1 = \frac{-2-8}{2} = -5 \\ \\ t_2 = \frac{-2+8}{2} = 3 \end{cases}$$
The equation t2+2t-15=0 has two real roots, t1=-5 and t2=3.
Therefore, the inequality t2+2t-15<0 is satisfied for values of t in the open interval (t1, t2)=(-5,3).
$$ -5 < t < 3 $$
Having obtained the solution in terms of the auxiliary variable t, return to the original variable x.
Since t=x3, it follows that x=3√t.
$$ - \sqrt[3]{5} < x < \sqrt[3]{3} $$
Note. The auxiliary variable is defined by t=x3, $$ t = x^3 $$ therefore, to recover x from t, apply the cube root to both sides of the equation $$ \sqrt[3]{t} = \sqrt[3]{x^3} $$ $$ \sqrt[3]{t} = x $$
Consequently, the original inequality x6 + 2x3 -15 < 0 is satisfied in the interval (-3√5, 3√3).
And so on.
