Geometric Vectors
What is a geometric vector?
A geometric vector is a set of equivalent directed segments.
In mathematics, a geometric vector is an abstract concept that highlights the common quality in a family of equivalent segments.
Understanding Equivalent Directed Segments
Given two directed segments AB and CD, they are considered equivalent if they share the same direction, sense, and length (also known as scalar magnitude or modulus).
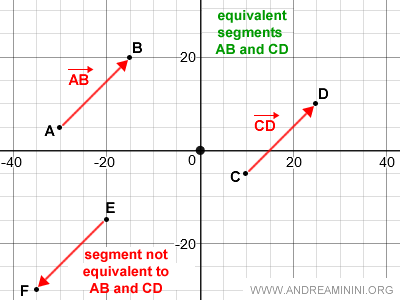
Note. The segments AB and CD are equivalent because they have the same direction, sense, and length. Conversely, segment EF is not equivalent to AB and CD because, although it shares the same direction and length, it has a different sense.
The equivalence between two directed segments is expressed as follows:
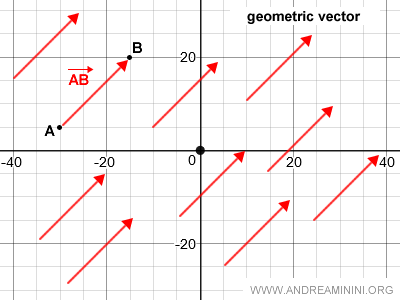
Translating a directed segment AB on the Cartesian plane generates infinitely many equivalent segments.
The collection of all segments equivalent to AB, created through translation, defines a geometric vector.
Therefore, it can be stated that
Given a direction, sense, and magnitude, there exists one and only one geometric vector with these characteristics.
In conclusion, a geometric vector is an abstract concept that represents the common quality in a family of equivalent segments.
Difference Between Free and Applied Vectors
A vector can be either applied or free.
- An applied vector is associated with a specific point of origin (O).
- A free vector is not bound to any specific point of origin.
A free geometric vector is the collection of all infinite vectors equivalent to vector AB (the class representative).
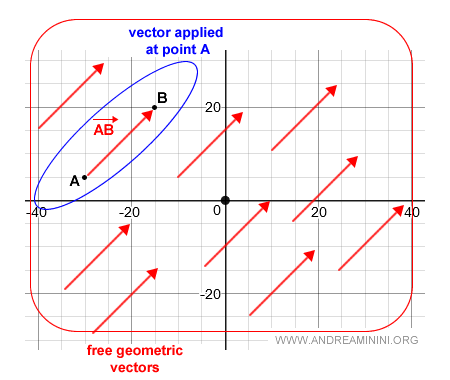
A free geometric vector represents the equivalence class (equipollence) of the applied vector AB at a point.
Note. The reference applied vector (class representative) is entirely arbitrary.
The set of all free vectors in a plane is known as the quotient set.
How to Add Geometric Vectors
You can add two free geometric vectors using the parallelogram method by positioning both vectors at the same origin (O).
A Practical Example
On a plane, two geometric vectors, AB and CD, belong to different equivalence classes.
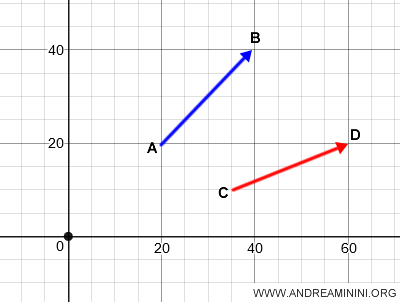
To add them, I reposition both vectors so they share the same origin.
Once aligned, the vectors AB and CD, now originating from O, become OB and OD.
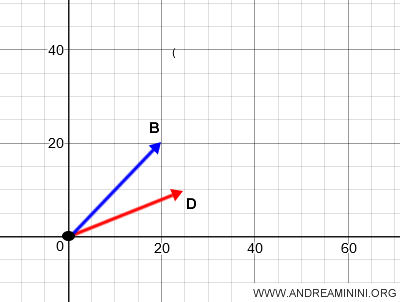
Which origin should you choose? If the plane has a designated origin O, using it is the best choice as it simplifies calculations.
Now, I add the two vectors OB and OP using the parallelogram method.
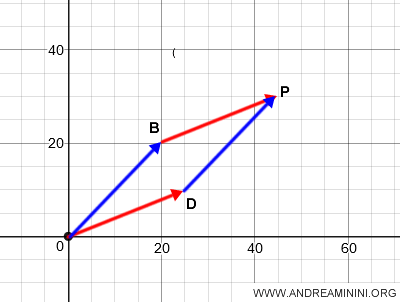
The sum of vectors OB and OD results in vector OP.
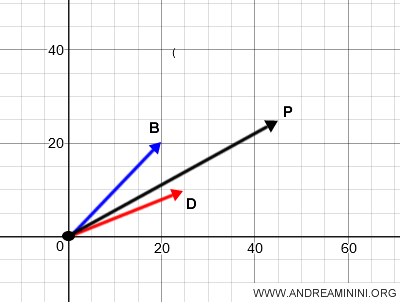
In conclusion, vector OP represents the equivalence class of the free geometric vector AB + CD.
When applied at every point on the plane, vector OP defines the free geometric vector OP.
