How to Determine the Equation of an Ellipse Given a Point and a Vertex
To write the equation of an ellipse centered at the origin, given a vertex and a point, we substitute the data into the general equation: $$\frac{x^2}{a^2} + \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1 $$
A Practical Example
Consider an ellipse centered at the origin $ O(0,0) $ with a vertex at $ V(-3,0) $ and passing through the point $ P \left( - \frac{3\sqrt{2}}{2}, -2 \right) $.
The vertex $ V(-3,0) $ lies on the x-axis.
Since the vertices are symmetrical about the origin, the other horizontal vertex is $ V(3,0) $.
The distance between the vertex $ V(-3,0) $ and the origin $ O(0,0) $ is the length of the horizontal semi-major axis.
$$ a = \sqrt{(x_v - x_o)^2 + (y_v - y_o)^2} $$
$$ a = \sqrt{(-3 - 0)^2 + (0 - 0)^2} $$
$$ a = \sqrt{9} $$
$$ a = 3 $$
Now, let's write the general equation of the ellipse.
$$\frac{x^2}{a^2} + \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1 $$
Substitute the length of the horizontal semi-major axis $ a = 3 $.
$$\frac{x^2}{3^2} + \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1 $$
$$\frac{x^2}{9} + \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1 $$
Next, substitute $ x $ and $ y $ with the coordinates of point $ P \left( - \frac{3\sqrt{2}}{2}, -2 \right) $.
$$\frac{\left( - \frac{3\sqrt{2}}{2} \right)^2}{9} + \frac{(-2)^2}{b^2} = 1 $$
$$\frac{ \frac{9 \cdot 2}{4} }{9} + \frac{4}{b^2} = 1 $$
$$\frac{ \frac{18}{4} }{9} + \frac{4}{b^2} = 1 $$
$$\frac{ \frac{9}{2} }{9} + \frac{4}{b^2} = 1 $$
$$ \frac{9}{2} \cdot \frac{1}{9} + \frac{4}{b^2} = 1 $$
$$ \frac{1}{2} + \frac{4}{b^2} = 1 $$
Now we solve for $ b $, the length of the vertical semi-major axis.
$$ \frac{4}{b^2} = 1 - \frac{1}{2} $$
$$ \frac{4}{b^2} = \frac{1}{2} $$
$$ b^2 = 2 \cdot 4 $$
$$ b^2 = 8 $$
$$ b = \sqrt{8} $$
$$ b = 2\sqrt{2} $$
Since $ a > b $, the major axis of the ellipse is horizontal.
Once we have the lengths of the semi-major axes $ a = 3 $ and $ b = 2\sqrt{2} $, we substitute them into the general equation of the ellipse.
$$\frac{x^2}{a^2} + \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1 $$
$$\frac{x^2}{3^2} + \frac{y^2}{(2\sqrt{2})^2} = 1 $$
$$\frac{x^2}{9} + \frac{y^2}{4 \cdot 2} = 1 $$
$$\frac{x^2}{9} + \frac{y^2}{8} = 1 $$
$$ \frac{8x^2 + 9y^2}{72} = 1 $$
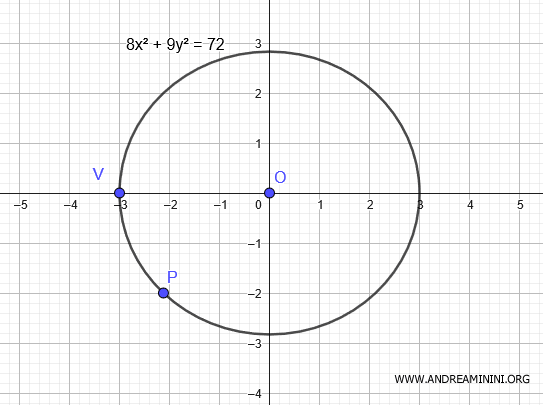
$$ 8x^2 + 9y^2 = 72 $$
This is the equation of the ellipse centered at the origin $ O(0,0) $, with a vertex at $ V(-3,0) $ and passing through the point $ P \left( - \frac{3\sqrt{2}}{2}, -2 \right) $.
And that's it.
