Multiplying a Definite Integral by a Constant
Multiplying the definite integral of a function \( f(x) \) over an interval [a, b] by a constant \( k \) is equivalent to integrating the product \( k \cdot f(x) \) over the same interval:
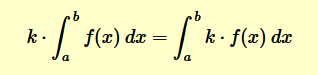
This property of definite integrals is especially useful when simplifying expressions during integration.
A Practical Example
Let’s consider the definite integral of the function \( f(x) = 2x \) over the interval [2, 5]:
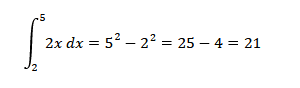
Now let’s compute the integral of the same function multiplied by a constant \( k = 2 \):
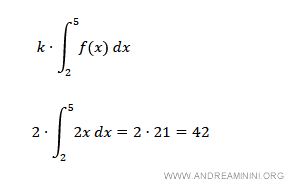
Alternatively, we can compute the integral of the function \( k \cdot f(x) \) directly over the interval [2, 5]:
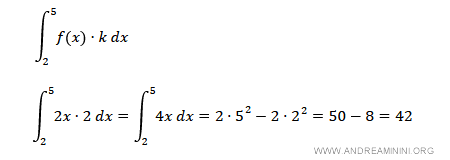
As expected, both approaches yield the same result.
Proof
If the function \( f(x) \) is Riemann integrable on the interval [a, b], then for any \( \epsilon > 0 \), there exists a partition \( P \) such that the difference between the upper and lower Darboux sums is less than \( \epsilon / 2 \):
![]()
Now consider the function \( k \cdot f(x) \), where \( k \geq 1 \):
![]()
The corresponding lower and upper Darboux sums satisfy:
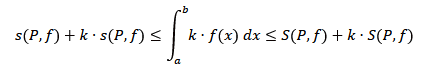
We now need to show that the following inequality holds:
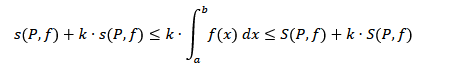
To do so, we examine the difference between the two sides:
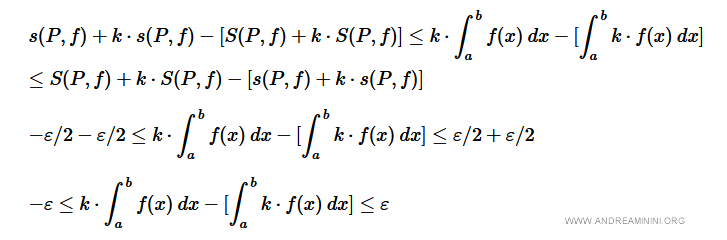
This proves that for any arbitrary \( \epsilon > 0 \), the inequality is satisfied, confirming that: $$ k \cdot \int_a^b f(x)\, dx = \int_a^b k \cdot f(x)\, dx $$
And so on.
