Equation of a Hyperbola Given an Asymptote and a Point
To find the equation of a hyperbola centered at the origin, given the equation of an asymptote $ y = \frac{b}{a} x $ and the coordinates $ P(x_0;y_0) $ of a point on the hyperbola, follow these steps:
First, identify the transverse axis, which is the axis along which the foci are located, to determine the standard form of the hyperbola's equation:
- If the transverse axis is the x-axis, the equation of the hyperbola is $$ \frac{x^2}{a^2} - \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1 $$
- If the transverse axis is the y-axis, the equation of the hyperbola is $$ \frac{x^2}{a^2} - \frac{y^2}{b^2} = -1 $$
Next, set up a system of equations using the standard form of the hyperbola and the asymptote equation:
$$ \begin{cases} y = \pm \frac{b}{a} x \\ \\ \frac{x^2}{a^2} - \frac{y^2}{b^2} = \pm 1 \end{cases} $$
Substitute $ x $ and $ y $ with the coordinates of the given point $ P(x_0;y_0) $ in the standard form equation:
$$ \begin{cases} y = \pm \frac{b}{a} x \\ \\ \frac{x_0^2}{a^2} - \frac{y_0^2}{b^2} = \pm 1 \end{cases} $$
By solving this system, you can determine the lengths of the semi-axes $ a $ and $ b $, which are necessary to write the equation of the hyperbola.
A Practical Example
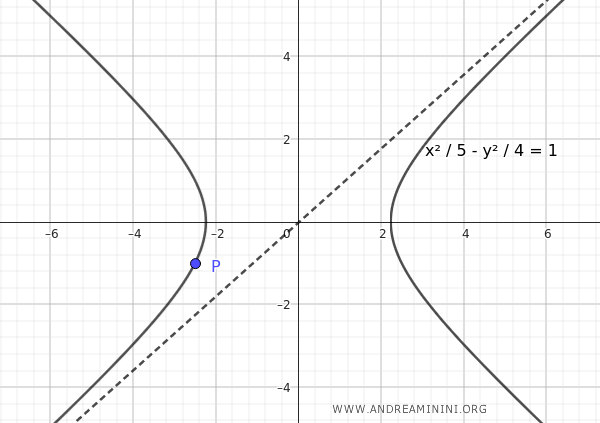
Let's find the equation of a hyperbola centered at the origin with foci on the x-axis that passes through the point $ P\left( - \frac{5}{2}, -1 \right) $ and has an asymptote given by $ y= \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} x $.
Since the foci are on the x-axis, the standard form of the hyperbola's equation is:
$$ \frac{x^2}{a^2} - \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1 $$
Substituting the coordinates of the point $ P\left( - \frac{5}{2}, -1 \right) $ into the equation, we have:
$$ \frac{\left( - \frac{5}{2} \right)^2}{a^2} - \frac{(-1)^2}{b^2} = 1 $$
$$ \frac{\frac{25}{4}}{a^2} - \frac{1}{b^2} = 1 $$
$$ \frac{25}{4a^2} - \frac{1}{b^2} = 1 $$
Next, we set up a system of equations using the asymptote and the hyperbola equations with the known point:
$$ \begin{cases} y= \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} x \\ \\ \frac{25}{4a^2} - \frac{1}{b^2} = 1 \end{cases} $$
Given that the asymptote can be written as $ y = \frac{b}{a} x $, we can write:
$$ \begin{cases} \frac{b}{a} x = \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} x \\ \\ \frac{25}{4a^2} - \frac{1}{b^2} = 1 \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} \frac{b}{a} = \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} \\ \\ \frac{25}{4a^2} - \frac{1}{b^2} = 1 \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} b = \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} a \\ \\ \frac{25}{4a^2} - \frac{1}{b^2} = 1 \end{cases} $$
Substituting $ b = \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} a $ into the second equation gives:
$$ \begin{cases} b = \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} a \\ \\ \frac{25}{4a^2} - \frac{1}{\left( \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} a \right)^2} = 1 \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} b = \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} a \\ \\ \frac{25}{4a^2} - \frac{1}{\frac{4a^2}{5}} = 1 \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} b = \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} a \\ \\ \frac{25}{4a^2} - \frac{5}{4a^2} = 1 \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} b = \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} a \\ \\ \frac{25 - 5}{4a^2} = 1 \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} b = \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} a \\ \\ \frac{20}{4a^2} = 1 \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} b = \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} a \\ \\ \frac{5}{a^2} = 1 \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} b = \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} a \\ \\ a^2 = 5 \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} b = \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} a \\ \\ a = \sqrt{5} \end{cases} $$
With $ a = \sqrt{5} $ determined, substitute this value into the first equation to find $ b $:
$$ \begin{cases} b = \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} \cdot \sqrt{5} \\ \\ a = \sqrt{5} \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} b = 2 \\ \\ a = \sqrt{5} \end{cases} $$
Now that we know the semi-axes $ a = \sqrt{5} $ and $ b=2 $, we can complete the equation of the hyperbola:
$$ \frac{x^2}{a^2} - \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1 $$
$$ \frac{x^2}{(\sqrt{5})^2} - \frac{y^2}{2^2} = 1 $$
$$ \frac{x^2}{5} - \frac{y^2}{4} = 1 $$
This is the equation of the hyperbola centered at the origin with its foci on the x-axis, passing through the point $ P\left( - \frac{5}{2}, -1 \right) $ and having an asymptote $ y = \frac{2}{\sqrt{5}} x $.
And so on.
