Finding the Equation of a Hyperbola Given a Focus and a Tangent Line
To find the equation of a hyperbola when given a focus and a tangent line, follow these steps:
- First, determine whether the transverse axis is along the x-axis $$ \frac{x^2}{a^2} - \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1 $$ or the y-axis $$ \frac{x^2}{a^2} - \frac{y^2}{b^2} = -1 $$. This will help you identify the standard form of the hyperbola's equation.
- Using the coordinates of the focus, apply the relationship $ c^2 = a^2 + b^2 $, where $ a $ and $ b $ are unknowns.
- Next, compare the equation of the tangent line with the tangent point formula $ \frac{x_0x}{a^2} - \frac{y_0y}{b^2} = 1 $ to find the coordinates $ (x_0; y_0) $ of the point of tangency in terms of $ a^2 $ and $ b^2 $. Substitute these into the equation of the tangent line to obtain another equation with $ a $ and $ b $ as unknowns.
- Finally, set up a system of equations using the two equations you’ve derived and solve for $ a^2 $ and $ b^2 $.
By following these steps, you can write the equation of the hyperbola.
Example
Consider a hyperbola centered at the origin with a focus at $ F( \sqrt{7},0 ) $ and a tangent line given by \(x - y = 1\).
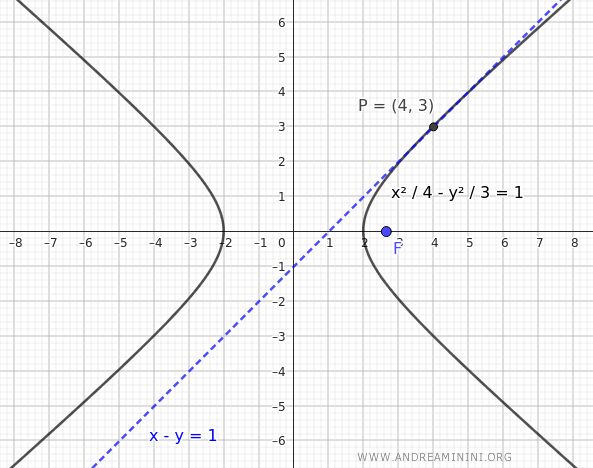
The focus is located on the x-axis, so the equation of the hyperbola is:
$$ \frac{x^2}{a^2} - \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1 $$
Here, \(a\) and \(b\) are the semi-axes of the hyperbola. Since the foci are along the x-axis, we use the relationship \(c^2 = a^2 + b^2\), where \(c\) is the focal distance.
The focus is at $ F( \sqrt{7},0 ) $, meaning the distance from the center to the focus is $ c=\sqrt{7} $.
$$ c = \sqrt{7} $$
Knowing that for a hyperbola $ c^2 = a^2 + b^2 $, we have:
$$ c^2 = a^2 + b^2 $$
$$ (\sqrt{7} )^2 = a^2 + b^2 $$
$$ a^2 + b^2 = 7 \quad \text{(Equation 1)} $$
Now, we need to find another equation involving $ a $ and $ b $.
The other piece of information provided is the tangent line, given by the equation \(x - y = 1\).
For a hyperbola, the equation of the tangent line at a point \((x_0, y_0)\) on the hyperbola is:
$$ \frac{x_0x}{a^2} - \frac{y_0y}{b^2} = 1 $$
By comparing this with the equation of the tangent line \(x - y = 1\), we get:
$$ \underbrace{ \frac{x_0}{a^2} }_1 x - \underbrace{ \frac{y_0}{b^2} }_1 y = 1 \Leftrightarrow x - y = 1 $$
This comparison tells us that the coefficients of x and y are:
$$ \frac{x_0}{a^2} = 1 \quad \text{and} \quad -\frac{y_0}{b^2} = -1 $$
From this, we conclude that
$$ x_0 = a^2 \quad \text{and} \quad y_0 = b^2 $$
So, the point of tangency \((x_0, y_0)\) on the hyperbola is \((a^2, b^2)\).
Since this point \((x_0, y_0) = (a^2, b^2)\) lies on both the hyperbola and the tangent line \(x - y = 1\), we substitute \(x = a^2\) and \(y = b^2\) into the tangent line equation:
$$ a^2 - b^2 = 1 \quad \text{(Equation 2)} $$
This gives us a second equation involving $ a $ and $ b $.
Now, we can set up a system of equations using the two equations we’ve found and solve the system:
$$ \begin{cases} a^2 + b^2 = 7 \\ \\ a^2 - b^2 = 1 \end{cases} $$
We solve for $ a^2 $ in the first equation and substitute it into the second equation:
$$ \begin{cases} a^2 = 7 - b^2 \\ \\ a^2 - b^2 = 1 \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} a^2 = 7 - b^2 \\ \\ 7 - b^2 - b^2 = 1 \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} a^2 = 7 - b^2 \\ \\ -2b^2 = 1 - 7 \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} a^2 = 7 - b^2 \\ \\ -2b^2 = -6 \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} a^2 = 7 - b^2 \\ \\ 2b^2 = 6 \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} a^2 = 7 - b^2 \\ \\ b^2 = \frac{6}{2} \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} a^2 = 7 - b^2 \\ \\ b^2 = 3 \end{cases} $$
After finding $b^2 = 3$, we substitute it back into the first equation to solve for $ a^2 $:
$$ \begin{cases} a^2 = 7 - 3 \\ \\ b^2 = 3 \end{cases} $$
$$ \begin{cases} a^2 = 4 \\ \\ b^2 = 3 \end{cases} $$
Now that we know $ a^2 = 4 $ and $ b^2 = 3 $, we can substitute these values into the standard equation of the hyperbola:
$$ \frac{x^2}{a^2} - \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1 $$
$$ \frac{x^2}{4} - \frac{y^2}{3} = 1 $$
This is the equation of the hyperbola with a focus at $ F( \sqrt{7},0 ) $ and a tangent line $ x - y = 1 $.

And that’s how it’s done.
