Unit Circle
What is the Unit Circle?
The unit circle is a circle with a radius of one (r=1), a starting point of the arcs (A), and a counterclockwise direction designated as positive.
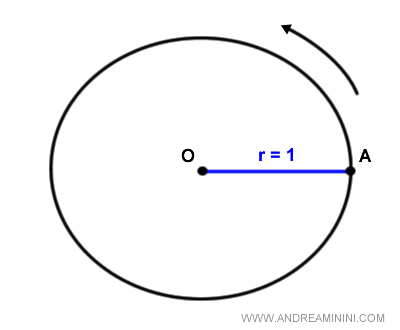
Point A is located at coordinates (x;y)=(1;0) and is known as the starting point of the arcs.
The unit circle is used to measure angles.
When any point P on the circle is chosen, the angle is defined by the vertex POA.
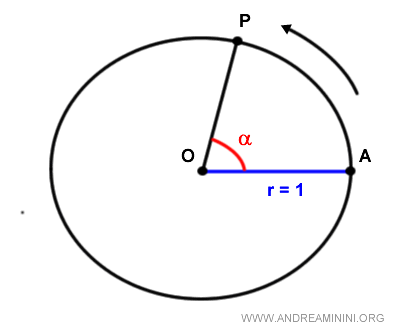
The angle is a directed angle because the unit circle has a predefined counterclockwise direction.
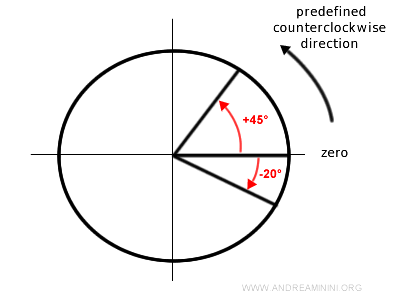
- The angle is positive if you move counterclockwise along the circle.
- The angle is negative if you move clockwise along the circle.
Note: The center of the circle coincides with the origin O of the Cartesian axes, which is the point at coordinates (0,0), taking the positive x-axis as the initial side of the directed angles. Thus, point A, the starting point of the arcs, is at coordinates (1,0) on the Cartesian plane.
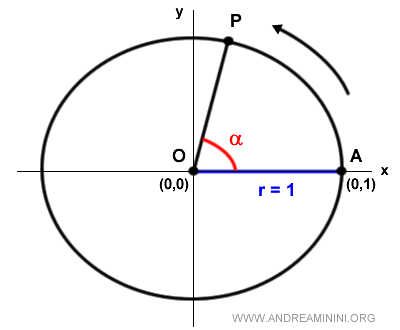
Since the radius is one (r=1), the equation of the unit circle on the Cartesian plane is $$ x^2 + y^2 = 1 $$
How to Measure the Angle's Magnitude
The angle's magnitude is measured in radians (rad) unless otherwise specified.
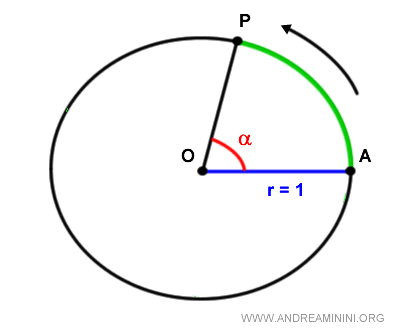
The angle's magnitude in radians is the ratio of the arc length AP on the unit circle to the radius OA.
$$ \alpha = \frac{\overline{AP}}{\overline{OA}} \ rad $$
Thus, in the unit circle, one radian is an arc AP with a length equal to the radius OA.
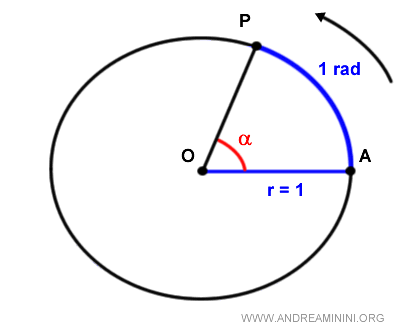
In this case, AP=OA, and the ratio is equal to 1:
$$ if \ \overline{AP} = \ \overline{OA} \ \Rightarrow \ \frac{\overline{AP}}{\overline{OA}} = 1 \ rad $$
The radian (rad) is the universally accepted unit for measuring angles.
Note: There are other units for measuring angles, such as degrees. However, an angle should be measured in sexagesimal degrees or decimal degrees only if explicitly specified in the problem.
Why Measure Arcs in Radians?
The length of an arc of a circle in radians is calculated using the formula
$$ l = \alpha \cdot r $$
Where l is the arc length, alpha is the angle, and r is the radius.
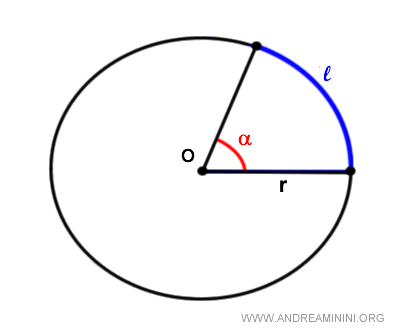
In a unit circle, the radius is one (r=1).
$$ l = \alpha \cdot 1 $$
Therefore, in the unit circle, the arc length in radians is the same as the angle measurement.
$$ l = \alpha $$
This is one of the advantages of measuring angles in radians (rad).
And so on.
