External Angles
External angles are formed by the intersection of one side of a polygon and the extension of an adjacent side.
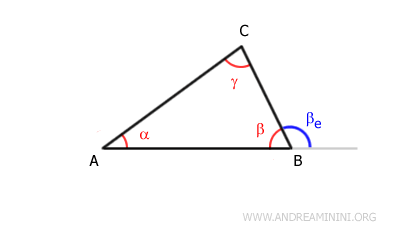
For example, consider triangle ABC.
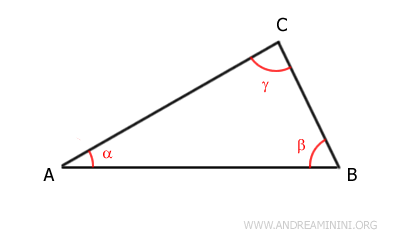
The triangle has three internal angles: α, β, and γ.
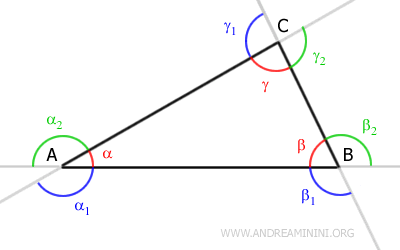
The triangle has the following external angles measured counterclockwise:
- Angle α1 is between the extension of side AC and side AB.
- Angle α2 is between side AC and the extension of side AB.
- Angle β1 is between side AB and the extension of side BC.
- Angle β2 is between the extension of side AB and side BC.
- Angle γ1 is between the extension of side BC and side AC.
- Angle γ2 is between side BC and the extension of side AC.
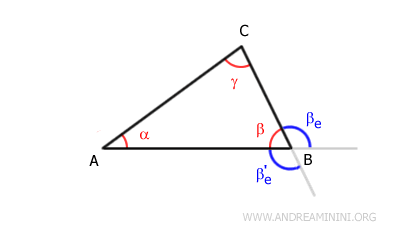
Each internal angle has two adjacent external angles. For example, the internal angle β has two adjacent external angles: βe and βe'.
Observations
Some useful observations about the sum of angles:
- Sum of external angles
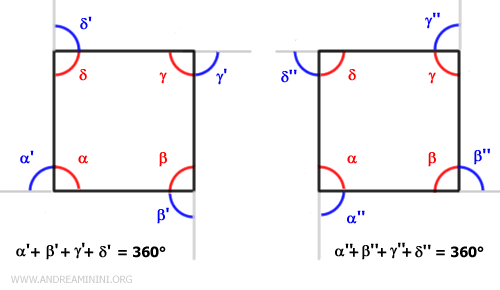
The sum of the external angles of a polygon is always 360°, regardless of the number of sides.Example: A square has 4 sides and 4 internal angles of 90°. Although each angle has two adjacent external angles, we only consider 4 external angles at a time, one at each vertex. The sum of these external angles is always 360°.
- External Angle Theorem
In a triangle, each external angle is greater than either of the non-adjacent internal angles.Example: In triangle ABC, the external angle βe is greater than each of the internal angles that are not adjacent to it: α and γ.
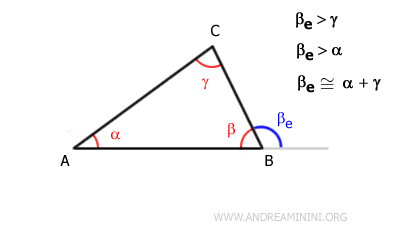
The internal angle β is not considered because it is adjacent to the external angle βe. - Relationship between internal and external angles
In any polygon, the sum of an internal angle and its adjacent external angle is always equal to a straight angle of 180°.Example: In triangle ABC, the sum of the internal angle β and the external angle βe forms a straight angle (180°).
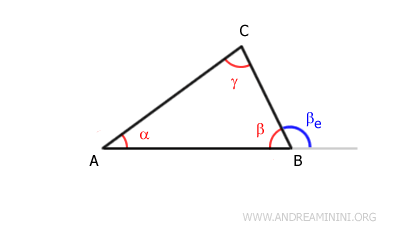
And so on.
