Derivative of the Cotangent Function
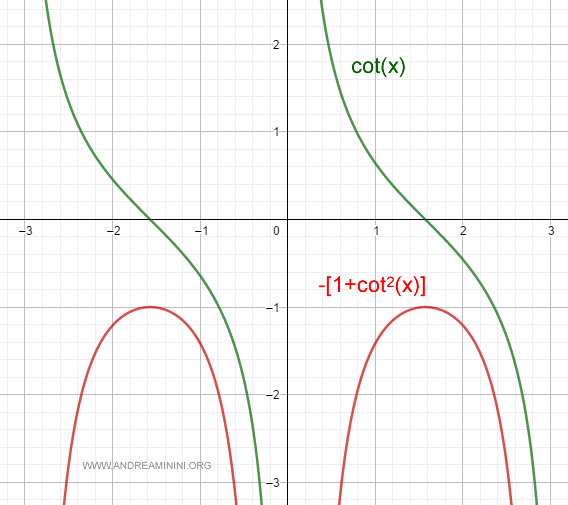
The derivative of the cotangent function is given by $$ D[\cot \: x] = \frac{-1}{\sin^2 \: x} = -\bigl(1 + \cot^2 \: x\bigr). $$
Proof
To derive this result, we start by recalling the trigonometric identity that expresses cotangent as the ratio of cosine to sine:
$$ \cot \: x = \frac{\cos \: x}{\sin \: x}. $$
Note. This derivation closely mirrors the one used for the derivative of the tangent function.
Hence, finding the derivative of the cotangent function amounts to differentiating the quotient of cosine and sine:
$$ D[\cot \: x] = D\left[ \frac{\cos \: x}{\sin \: x} \right]. $$
This is straightforward, given that we already know the derivatives of sine and cosine:
$$ D[\sin \: x] = \cos \: x $$
$$ D[\cos \: x] = -\sin \: x $$
Applying the quotient rule, we obtain:
$$ D[\cot \: x] = \frac{D[\cos \: x] \cdot \sin \: x - \cos \: x \cdot D[\sin \: x]}{\bigl(\sin \: x\bigr)^2}. $$
Substituting the derivatives of sine and cosine yields:
$$ = \frac{(-\sin \: x) \cdot \sin \: x - \cos \: x \cdot \cos \: x}{\bigl(\sin \: x\bigr)^2}. $$
This simplifies to:
$$ = \frac{-\sin^2 \: x - \cos^2 \: x}{\bigl(\sin \: x\bigr)^2}. $$
Factoring out the negative sign, we have:
$$ = \frac{ -\bigl(\sin^2 \: x + \cos^2 \: x\bigr) }{\bigl(\sin \: x\bigr)^2}. $$
From the fundamental Pythagorean identity, we know that $$ \sin^2 \: x + \cos^2 \: x = 1. $$
Therefore, the expression simplifies to:
$$ \frac{ -\bigl(\sin^2 \: x + \cos^2 \: x\bigr) }{\bigl(\sin \: x\bigr)^2} = \frac{-1}{\sin^2 \: x}. $$
According to a trigonometric identity that relates sine to cotangent, we have: $$ \sin \: x = \frac{1}{\sqrt{1 + \cot^2 \: x}}. $$
Substituting this identity leads to:
$$ \frac{-1}{\sin^2 \: x} = \frac{-1}{\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{1 + \cot^2 \: x}}\right)^2} = \frac{-1}{\frac{1}{1 + \cot^2 \: x}} = -\bigl(1 + \cot^2 \: x\bigr). $$
This completes the proof of the derivative formula for the cotangent function.