Derivative of the Arccosine Function
The derivative of the arccosine function is: $$ D[\arccos x] = \frac{-1}{\sqrt{1 - x^2}}. $$
This result can be derived using the rule for differentiating inverse functions.
Note. In trigonometry, the arccosine is the inverse function of the cosine on the interval $(0, \pi)$.
Understanding the Arccosine Function
The cosine function is not monotonic over its entire real domain:
$$ f(x) = \cos x $$
However, when restricted to the closed interval $[0, \pi]$, the cosine function becomes monotonic and strictly decreasing, with values ranging between $1$ and $-1$.
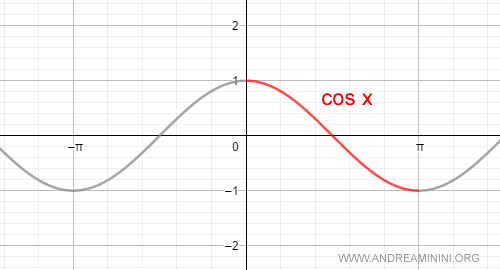
Because it is continuous and monotonic on $[0, \pi]$, the cosine function is also invertible on this interval.
The inverse of the cosine function is known as the arccosine function:
$$ f^{-1}(x) = \arccos x $$
Why is it called arccosine? It’s called arccosine because it measures the arc length - that is, the angle in degrees or radians on the unit circle - that corresponds to a given cosine value.
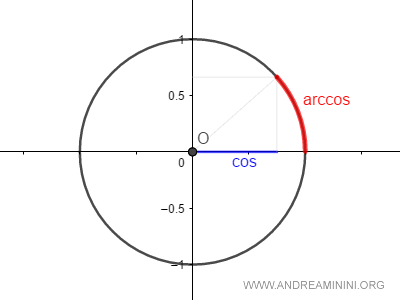
Since cosine and arccosine are inverse functions: $$ y = \cos x \\ x = \arccos y $$ Thus: $$ y = \cos(\arccos y) \\ x = \arccos(\cos x) $$
The domain of the arccosine function is the closed interval $[-1, 1]$.
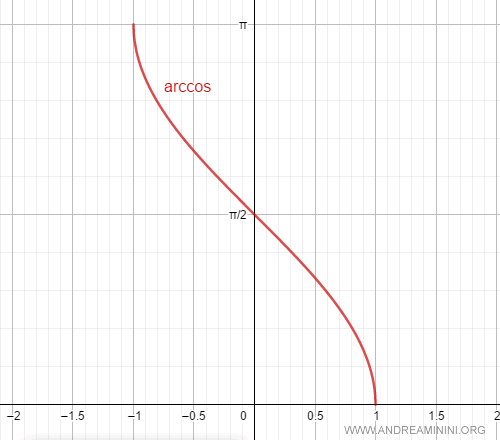
Therefore, the arccosine function is differentiable on the open interval $(-1, 1)$.
Proof and Explanation
The arccosine function is defined as the inverse of the cosine function:
$$ f^{-1}(f(y)) = \arccos x $$
where $f(y)$ is given by:
$$ f(y) = \cos y $$
To differentiate the arccosine function, we apply the inverse function differentiation rule:
$$ D[f^{-1}] = \frac{1}{D[f(y)]}. $$
Hence:
$$ D[\arccos x] = \frac{1}{D[\cos y]}. $$
Since the derivative of the cosine function is $-\sin y$, we have:
$$ D[\arccos x] = \frac{1}{- \sin y}. $$
Note. Recall the trigonometric identity: $$ \sin y = \sqrt{1 - \cos^2 y}. $$
Substituting this identity yields:
$$ D[\arccos x] = \frac{1}{- \sqrt{1 - \cos^2 y}}. $$
Which simplifies to:
$$ D[\arccos x] = - \frac{1}{\sqrt{1 - \cos^2 y}}. $$
Note. Since $$ y = \arccos x, $$ it follows that $$ \cos y = \cos(\arccos x) = x. $$ Therefore, we can substitute: $$ \cos^2 y = \cos^2(\arccos x) = x^2. $$
Thus:
$$ D[\arccos x] = - \frac{1}{\sqrt{1 - x^2}}. $$
This completes the proof of the derivative formula for the arccosine function.
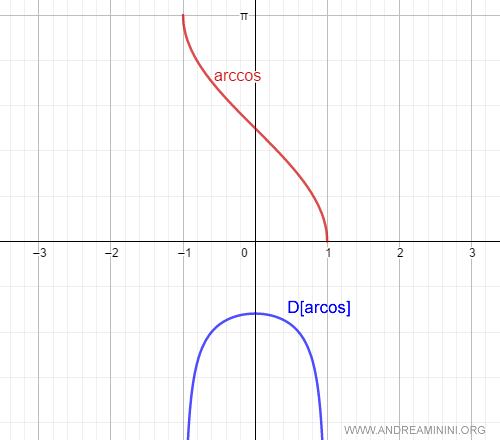
And so on.
