How to Find the Radius of a Circle
To find the radius of a circle from its equation in general form $$ x^2 + y^2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0 $$, use this formula: $$ r = \sqrt{(-\frac{D}{2})^2 + ( -\frac{E}{2} )^2 - F } $$
If the circle's equation is given in standard form, determining the radius is much easier.
\[ (x - h)^2 + (y - k)^2 = r^2 \]
In this case, the center and radius of the circle are:
- \( (h, k) \) are the coordinates of the circle's center.
- \( r \) is the radius of the circle.
When the circle's equation is in general form:
\[ x^2 + y^2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0 \]
The center \((h, k)\) of the circle can be found using these formulas:
$$ h = -\frac{D}{2} $$
$$ k = -\frac{E}{2} $$
where \(D\) and \(E\) are the coefficients of \(x\) and \(y\) in the general circle equation \( x^2 + y^2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0 \).
Thus, the center of the circle is at coordinates \((-D/2, -E/2)\).
The radius of the circle is given by the formula:
$$ r = \sqrt{(-\frac{D}{2})^2 + ( -\frac{E}{2} )^2 - F } $$
Alternatively, to find the radius and the center of a circle, you can convert the equation from general form to standard form by completing the square and adding the necessary terms. In standard form, \( (x - h)^2 + (y - k)^2 = r^2 \), the radius is simply calculated as \( r = \sqrt{r^2} \).
A Practical Example
Example 1
In this example, we have the circle's equation in standard form:
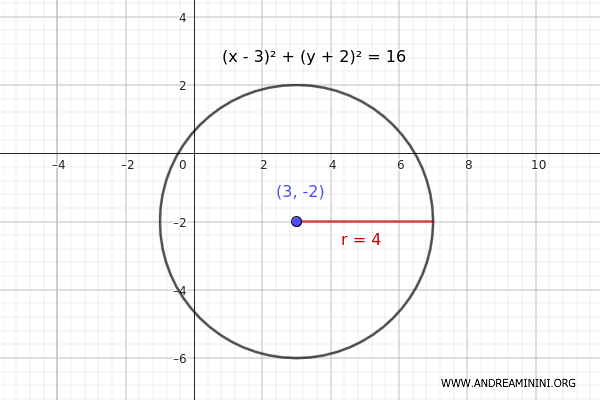
$$ (x - 3)^2 + (y + 2)^2 = 16 $$
Finding the radius and center is straightforward.
- The center of the circle is \( (3, -2) \).
- The term on the right-hand side is \( r^2 = 16 \).
To find the radius \( r \), we just take the positive square root of 16:
$$ r = \sqrt{16} = 4 $$
Therefore, the radius of the circle is 4.
Example 2
In this example, the circle's equation is not in standard form:
$$ x^2 + y^2 + 6x - 8y + 9 = 0 $$
Here, we can find the radius using the radius formula:
$$ r = \sqrt{(-\frac{D}{2})^2 + ( -\frac{E}{2} )^2 - F } $$
where the coefficients in the general equation \( x^2 + y^2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0 \) are D=6, E=-8, and F=9.
$$ r = \sqrt{(-\frac{6}{2})^2 + ( -\frac{-8}{2} )^2 - 9 } $$
$$ r = \sqrt{(-3)^2 + (4)^2 - 9 } $$
$$ r = \sqrt{9 + 16 - 9 } $$
$$ r = \sqrt{16 } $$
$$ r = 4 $$
Alternatively, we can find the radius by converting the general form of the circle's equation into the standard form.
We group the \( x \) and \( y \) terms:
$$ x^2 + y^2 + 6x - 8y + 9 = 0 $$
$$ (x^2 + 6x) + (y^2 - 8y) = -9 $$
We complete the square for \( x \) by adding and subtracting the term \( (\frac{6}{2})^2 \):
$$ (x^2 + 6x +(\frac{6}{2})^2) - (\frac{6}{2})^2 + (y^2 - 8y) = -9 $$
$$ (x^2 + 6x + 3^2) - 3^2 + (y^2 - 8y) = -9 $$
$$ (x + 3)^2 - 9 + (y^2 - 8y) = -9 $$
$$ (x + 3)^2 + (y^2 - 8y) = 0 $$
We complete the square for \( y \) by adding and subtracting the term \( (\frac{8}{2})^2 \):
$$ (x + 3)^2 + (y^2 - 8y + (\frac{8}{2})^2 ) - (\frac{8}{2})^2 = 0 $$
$$ (x + 3)^2 + (y^2 - 8y + 4^2 ) - 4^2 = 0 $$
$$ (x + 3)^2 + (y - 4)^2 = 4^2 $$
$$ (x + 3)^2 + (y - 4)^2 = 16 $$
Now the equation is in standard form, and the term on the right-hand side is \( r^2 = 16 \).
To calculate the radius, we simply take the square root of this term:
$$ r = \sqrt{16} = 4 $$
Therefore, the radius of the circle is 4.
Other Useful Formulas for Finding the Radius
Generally, the formula for finding the radius \( r \) of a circle depends on the information available.
Here are some common situations:
- If you know the circumference $$ r = \frac{C}{2\pi} $$ where \( C \) is the circumference.
- If you know the area $$ r = \sqrt{\frac{A}{\pi}} $$ where \( A \) is the area of the circle.
- If you know the coordinates of the endpoints \( (x_1, y_1) \) and \( (x_2, y_2) \) of the diameter, the radius is half the Euclidean distance between these points: $$ r = \frac{\sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}}{2} $$
These formulas allow you to calculate the radius of a circle in various situations. They are included for completeness.
And so on.
