Circumference
The circumference is the perimeter of a circle, a two-dimensional geometric figure made up of all points on a plane that are at a constant distance (known as the radius "r") from a fixed point O, called the center.
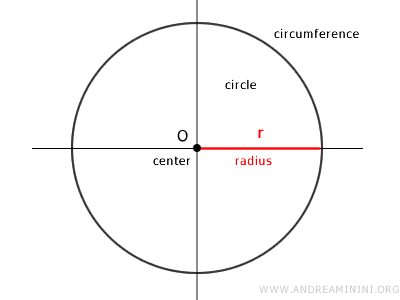
The circumference is the collection of points equidistant from the center.
The distance from any point on the circumference to the center (O) is known as the radius.
In other words, the circumference is the perimeter or outline of a circle, where the circle itself represents the area within the circumference.

The circle can also be described as the set of points at a distance from the center of the circumference that is less than or equal to the radius. What's the difference between a circumference and a circle? The circumference is the line that defines the edge of a flat shape, whereas the circle is the shape enclosed by this line. In other words, the circumference is the perimeter or edge of the circle, while the circle includes its interior as well.
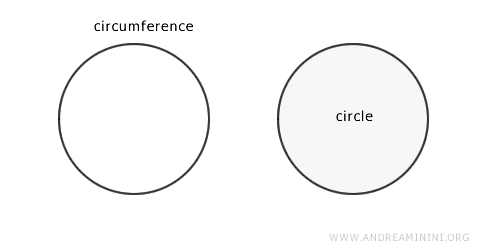
Thus, the circle is the flat shape that contains the points of the circumference and the points within it.
The length of the circumference (C) is determined by the formula 2πr
$$ C = 2 \pi r $$
Where r is the radius and π (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14.
Given that the diameter (d) is twice the radius d=2r, it can also be expressed as
$$ C = \pi \cdot d $$
What is pi? The ratio of a circumference's length to its diameter is a constant value, represented by the symbol π, known as pi, and is approximately 3.14. $$ π=3.14159 $$
The Formulas of the Circumference
The key formulas for calculating the measures of the circumference
- Circumference Length
The length of a circumference (or perimeter) is given by the formula 2πr, where π is the mathematical constant "pi," approximately equal to 3.14159, and "r" is the radius. $$ C = 2 \cdot \pi \cdot r $$ - Area
The area of the circle enclosed by a circumference is given by the formula $$ A = \pi \cdot r^2 $$ - Radius
The radius is equal to the circumference divided by 2π $$ r = \frac{C}{2\pi} $$ - Diameter
The diameter is the distance between two opposite points on the circumference, passing through the center. It is twice the radius. $$ d = 2r $$
The Radius
The radius of a circumference is a segment connecting the center O of the circumference with any point P on the circumference.
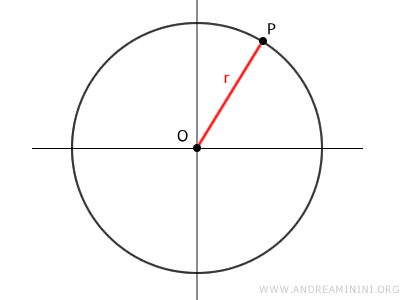
Therefore, there are infinitely many segments that identify the radius, and they are congruent because they are of equal length.
The formula to calculate the radius is as follows
$$ r = \frac{C}{2 \pi} $$
Knowing that the circumference equals twice the product of the radius and pi $$ C = 2 \pi r $$ dividing both sides of the equation by 2π gives the formula for the radius $$ \frac{C}{2 \pi} = \frac{2 \pi r}{2 \pi} $$ $$ \frac{C}{2 \pi} = r $$
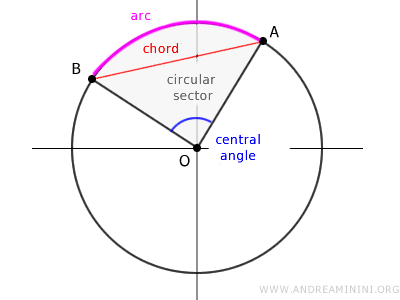
The Arcs
Any two points A and B on a circumference divide it into two parts called arcs.
An arc is a section of the circumference bounded by points A and B.
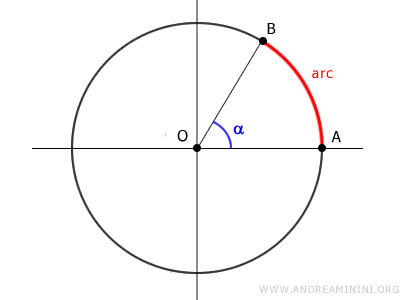
The length of the arc can be determined by considering the angle's amplitude α
$$ l_a = 2 \pi r \cdot \frac{ \alpha }{360°} $$
Where 2πr is the length of the circumference.
Thus, there is a close relationship between the length of the arc, the angle's amplitude, and the radius of the circumference.
Example. If a circumference has a radius of 10 cm and the angle's amplitude is 90°, the length of the arc can be calculated as follows $$ l_a = 2 \pi \cdot 10 \cdot \frac{ 90 }{360} = 2 \pi \cdot 10 \cdot \frac{1}{4} = 5 \pi $$
Chords
A chord of a circumference is any segment with endpoints at two distinct points A and B on the circumference.
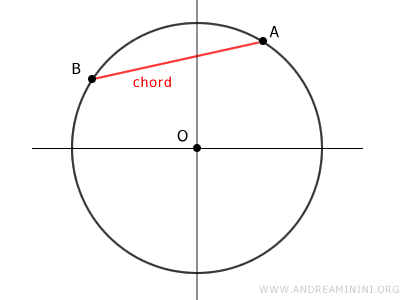
If the chord also passes through the center, it is called the diameter of the circumference.
The Diameter
The diameter is a segment that connects two distinct points on the circumference and passes through the center of the circumference.
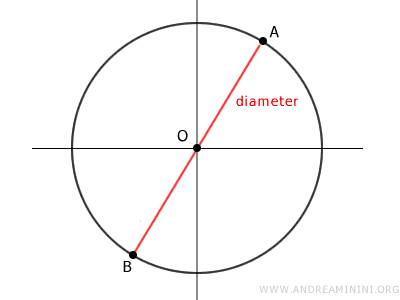
In essence, the diameter is a special chord that crosses the center of the circumference. It is the longest chord in a circumference.
The length of the diameter is equal to 2r, twice the radius.
$$ d = 2r $$
There are infinitely many segments that can represent the diameter of a circumference, all congruent to each other because they share the same length.
The Circumference Postulate
Given a point O and any segment AB in a plane, there exists one and only one circumference with center at point O and radius equal to segment AB
The Equation of the Circumference
The standard form equation of the circumference in the Cartesian plane is as follows:
$$ (x - x_0)^2 + (y - y_0)^2 = r^2 $$
Where (x0; y0) are the coordinates of the center O of the circumference and r is the radius of the circumference.
Alternatively, the general equation of the circumference can be written as
$$ x^2+ y^2+ ax +by+ c = 0 $$
Where the parameters are a=-2x0, b=-2y0, c=x02+y02-r2
In this case, the coordinates (x0; y0) of the center of the circumference are:
$$ (x_0 ; y_0) = ( - \frac{a}{2} ; - \frac{b}{2} ) $$
While the radius is obtained as follows
$$ r = \sqrt{ ( - \frac{a}{2} )^2 + ( - \frac{b}{2} )^2 - c } $$
The equation of the circumference can also be written in this equivalent explicit form $$ y = y_0 \pm \sqrt{r^2 - (x-x_0)^2 } $$
It's important to note that the equation x2+y2+ax+by+c=0 does not always represent a circle.
The equation represents a circle with center C only if this reality condition is met:
$$ \left( -\frac{a}{2} \right)^2 + \left( -\frac{b}{2} \right)^2 - c \ge 0 $$
This is because the radius (r) measures the distance between two points, which is a length $ \overline{OP} $ and must always be a non-negative number ( r ≥ 0 ).

In other words, the equation is a necessary but not sufficient condition for drawing a circle.
In the specific case where the radius is zero (r=0), the circle is known as a degenerate circle.
Note. If the distance were negative, there would be a negative number under the square root, and it could not be solved in the field of real numbers. $$ r = \sqrt{\left( -\frac{a}{2} \right)^2 + \left( -\frac{b}{2} \right)^2 - c} $$
Example
I want to draw a circumference with the center at point (x;y)=(1;3) and radius r=2.
In this case x0=1 and y0=3
$$ (x - x_0)^2 + (y - y_0)^2 = r^2 $$
$$ (x - 1)^2 + (y - 3)^2 = r^2 $$
The radius of the circumference is r=2
$$ (x - 1)^2 + (y - 3)^2 = 2^2 $$
$$ (x - 1)^2 + (y - 3)^2 = 4 $$
This equation is satisfied by all the points that are 4 units away from point (1;3) on the plane.
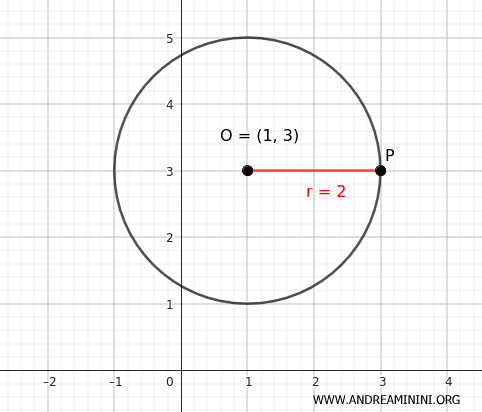
In this way, I have outlined the circumference I intended to construct.
Observations
Some observations about circumferences
- A circumference is symmetric relative to its center and any line passing through the circle.
- The circumference is convex, because any two points on the circumference are joined by a segment that is entirely contained within it.
- The principles of congruence in a circumference
In a circumference, if two chords, two arcs, two circular sectors, two circular segments, or two central angles are congruent, then all the others are congruent as well. This happens because these sizes are correspondingly biunivocal. For example, a central angle corresponds to an arc and vice versa.
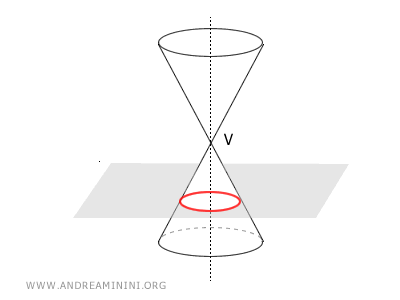
- Circles: A Member of the Conic Sections Family
Circles belong to the family of conic sections, as they are formed by intersecting a cone with a plane perpendicular to the cone’s axis. This intersection creates a circle on the surface of the cone.
And so on
