Perpendicular Bisectors of a Triangle
A perpendicular bisector of a triangle is a line that passes through the midpoint of a side and is perpendicular to that side.
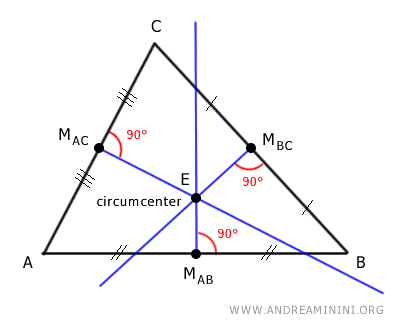
In a triangle, there are three perpendicular bisectors, one for each side. These lines are also known as perpendicular medians.
A perpendicular bisector is a line that goes through the midpoint of a triangle's side (MAB, MBC, MAC), dividing the side into two equal parts and forming a right angle of 90° with the side.
Every triangle has three perpendicular bisectors, one for each side.
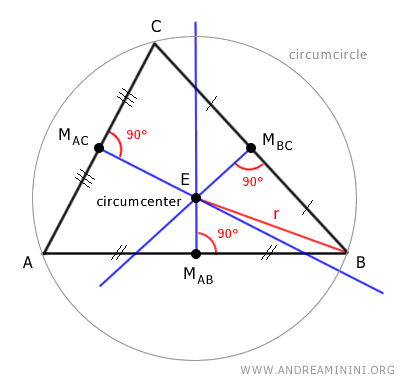
These three perpendicular bisectors intersect at a single point called the circumcenter (E) of the triangle.
The circumcenter (E) is the center of the circumscribed circle, known as the circumcircle, which passes through all three vertices (A, B, C) of the triangle.
And so forth.
