Diagonal Matrix
A square matrix is known as a diagonal matrix when all elements outside the main diagonal are zero.
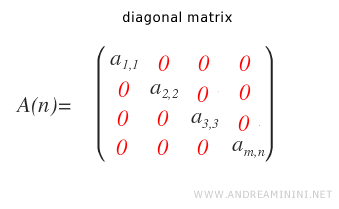
In other words, if \( i \neq j \), then \( a_{ij} = 0 \).
Example
For example, consider a diagonal matrix of order 3, which has three rows and three columns.
As shown, all elements above and below the main diagonal are zero.
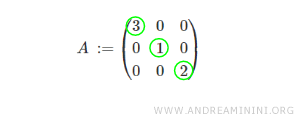
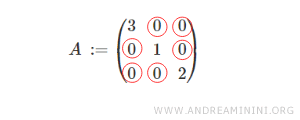
Note: Elements on the main diagonal may be either zero or non-zero.
Therefore, a diagonal matrix can also be considered both a lower and an upper triangular matrix.
In mathematics, the set of diagonal matrices of order \( n \) with real-number entries is denoted by \( D \), where \( n \) indicates the matrix order and \( R \) represents real coefficients.
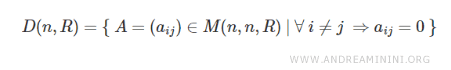
In summary, diagonal matrices are fundamental in linear algebra, with applications spanning various branches of mathematics and science.
