Line
In geometry, a line is a continuous one-dimensional entity that has length but no width or depth.
It is one of the fundamental concepts in geometry.
Lines are composed of an infinite sequence of points arranged in a continuous manner.

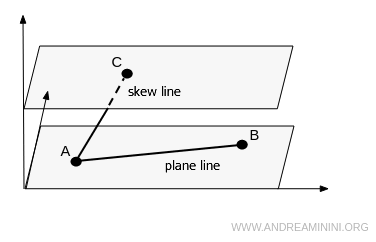
If the continuous movement of points occurs on a plane, the line is called a plane line.
If the line consists of points on different planes, it is called a skew line.
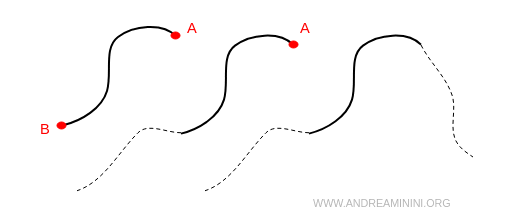
A line can be bounded by two endpoints A and B, have only one endpoint A, or have no endpoints at all.
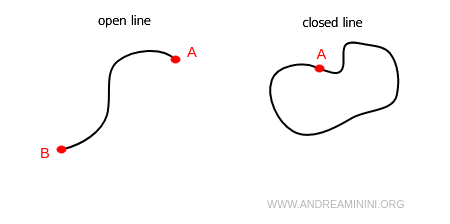
If the endpoints coincide, it is called a closed line; otherwise, it is an open line.
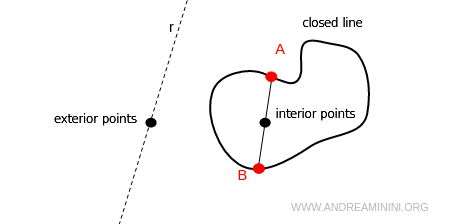
A closed line divides the plane into two regions:
- Interior points
These are the points that lie on the segments formed by joining any two points on the line. - Exterior points
These are the points that belong to the plane but are not on the segments between two points of the line.
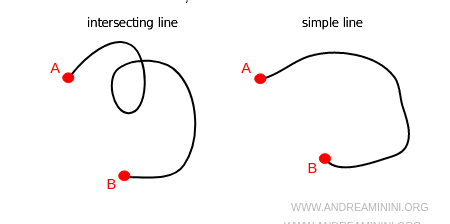
An open or closed line is called an intersecting line if it passes through the same point multiple times; otherwise, it is called a simple line.
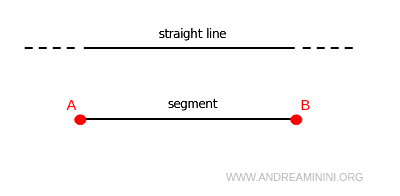
If all its points are aligned, the line is called a straight line if it has no endpoints, or a segment if it is bounded by two endpoints.
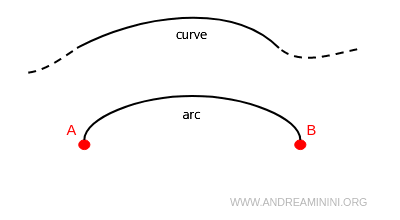
In all other cases, the line is called a curve or simply a curved line.
A curve bounded by two endpoints is called an arc.
Therefore, straight lines, rays, and segments are specific cases of lines.
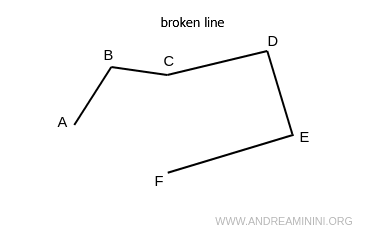
A line composed of a sequence of segments in different directions is called a broken line or polygonal line.
- Broken line
A sequence of straight segments, called sides, each connected at one endpoint to the next segment. A broken line does not need to close on itself. In other words, a broken line can be open or closed.
- Polygonal line
A closed broken line, meaning the last segment ends where the first segment started. Therefore, a polygonal line is always closed.
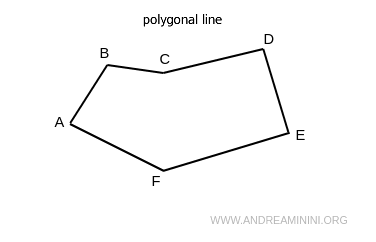
If there are no intersections, the closed polygonal line is called a polygon.
Essentially, the main difference between the two is that a broken line can be open or closed, while a polygonal line is always closed.
Note: In Euclidean geometry, a line is often defined as the shortest path between two points. However, this concept is more accurately termed distance. It is the segment that connects any two points on the curve.
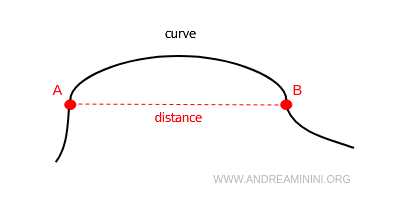
Among any distinct points A and B on the curve, there are infinite curves but only one straight line. The distance is the segment of this straight line bounded by the two endpoints A and B.
And so on.
