Composite Functions
What is a composite function?
A function is called a composite function when its domain matches the range (codomain) of another function. $$ h(x) = f(g(x)) $$ This is read as f of g of x.
The composite function is also commonly written as:
$$ h = f \circ g $$
which is read as f composed with g.
The codomain of g serves as the domain of f.
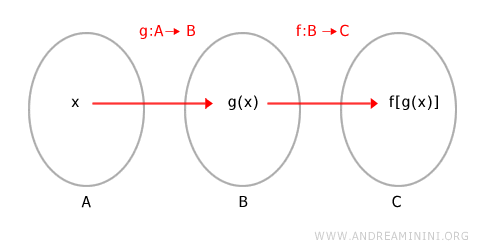
Note. Set A represents the domain of g. Set B is the range of g - that is, both the codomain of g and the domain of f. Set C contains the outputs of f, which are also the outputs of the composite function f[g(x)].
A practical example
Consider the following two functions:
$$ f(x) = \frac{1}{x} $$
$$ g(x) = \sin x $$
The composite function h(x), defined as f(g(x)), is:
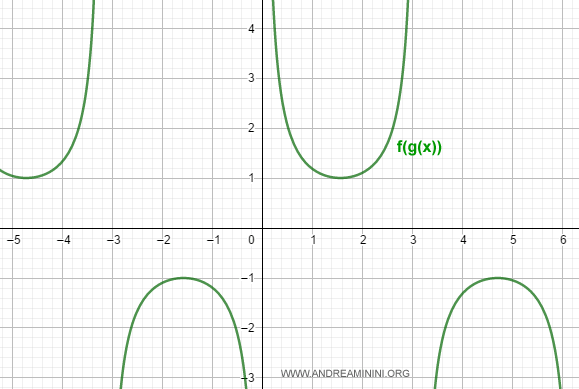
$$ h(x) = f(g(x)) = \frac{1}{g(x)} = \frac{1}{\sin x} $$
In this case, the domain of f must match the range of g, which is the interval [0,1].
The graph of the composite function f(g(x)) is shown below:
Properties of composite functions
Key properties of composite functions include:
- Composite functions are not commutative. In general: $$ g[f(x)] \ne f[g(x)] $$
Example. Consider the two functions: $$ f(x) = x+1 $$ $$ g(x) = 2x+3 $$ The composite function g[f(x)] is: $$ g(f(x)) = g(x+1) = 2(x+1) + 3 = 2x + 5 $$ On the other hand, the composite function f[g(x)] is: $$ f(g(x)) = f(2x+3) = (2x+3) + 1 = 2x + 4 $$ Clearly, these are two distinct functions.
- Composite functions do satisfy the associative property: $$ h \circ (g \circ f) = (h \circ g) \circ f $$
Example. Let’s consider three functions: $$ f(x) = x+1 $$ $$ g(x) = 2x+3 $$ $$ h(x) = -x $$ The composite function h o (g o f) is: $$ h \circ (g \circ f) = h \circ [2(x+1) + 3] = h \circ [2x + 5] = -[2x + 5] = -2x - 5 $$ Likewise, the composite function (h o g) o f is: $$ (h \circ g) \circ f = -(2x + 3) \circ f = -2x - 3 \circ f = -2(x + 1) - 3 = -2x - 5 $$ The result is the same in both cases.
- If the range of f[g(x)] coincides with the domain of g(x) - in other words, if A = C -
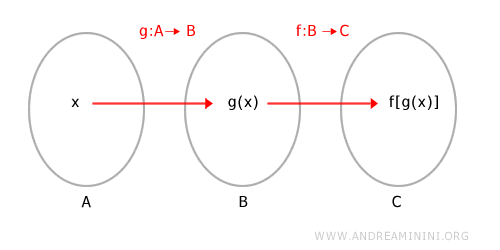
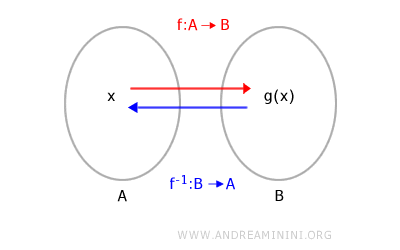
then it is possible to define the composite function g[f(x)] as well. However, in general: $$ f[g(x)] \ne g[f(x)] $$ because composite functions do not obey the commutative property. - The composition of a function f:A→B with its inverse function f-1:B→A returns each input x to itself: $$ f^{-1}[f(x)] = x $$ This specific composition is called the identity function.
And so on.
