Quadratic Function
A quadratic function is any function that can be written in the form $$ y = ax^2 + bx + c $$ where the leading coefficient \( a \neq 0 \).
The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola.
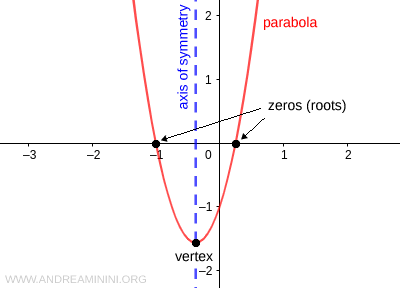
The axis of symmetry of the parabola is a vertical line:
$$ x = - \frac{b}{2a} $$
The vertex of the parabola is the point V:
$$ V \begin{pmatrix} \ - \frac{b}{2a} \ ; \ - \frac{b^2-4ac}{4a} \ \end{pmatrix} $$
The roots (or zeros) of a quadratic function are the values of \( x \) where the parabola intersects the x-axis. They are called “zeros” because at these points the function takes the value \( y=0 \).
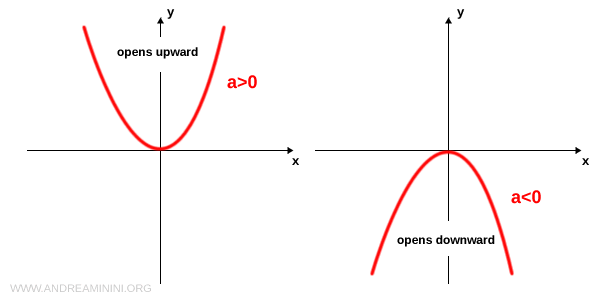
The concavity of the parabola depends only on the sign of the leading coefficient \( a \):
- a>0
If \( a>0 \), the parabola opens upward. - a<0
If \( a<0 \), the parabola opens downward.
The width of the parabola is determined by the absolute value of \( a \).
The larger the absolute value |a|, the narrower the parabola; the smaller |a| is, the wider it becomes.

Note. By the parabola’s opening we mean the distance between its curve and the axis of symmetry. A smaller absolute value of |a| makes the parabola spread out, moving closer to its axis of symmetry.
A Worked Example
Consider the quadratic function:
$$ y = 4x^2 + 3x - 1 $$
Since the leading coefficient \( a = 4 \) is positive, the parabola opens upward.
To find the roots (the x-intercepts), we solve the associated quadratic equation:
$$ 4x^2 + 3x - 1 = 0 $$
The discriminant is positive:
$$ \Delta = b^2 - 4ac = 3^2 - 4(4)(-1) = 9 + 16 = 25 $$
So the equation has two distinct real solutions:
$$ x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{\Delta} }{2a} = \frac{-3 \pm \sqrt{25}}{2(4)} = \frac{-3 \pm 5}{8} = \begin{cases} x_1 = \frac{-3 - 5}{8} = -1 \\ \\ x_2 = \frac{-3 + 5}{8} = \tfrac{1}{4} \end{cases} $$
Thus, the roots of the quadratic function are \( x_1 = -1 \) and \( x_2 = \tfrac{1}{4} \).
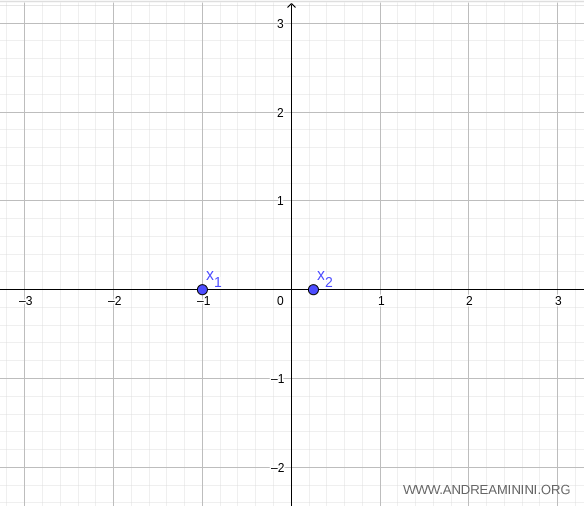
Now let’s determine the axis of symmetry, given \( a=4, b=3, c=-1 \):
$$ x = - \frac{b}{2a} = - \frac{3}{2 \cdot 4} = - \frac{3}{8} $$
The axis of symmetry is the vertical line perpendicular to the x-axis at \( x = -\tfrac{3}{8} \).
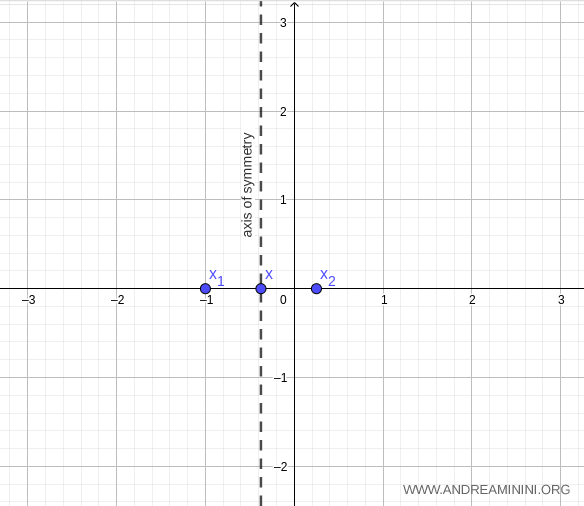
Next, we find the vertex of the parabola:
$$ V \begin{pmatrix} \ - \frac{b}{2a} \ ; \ - \frac{b^2-4ac}{4a} \ \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} - \tfrac{3}{8} ; - \tfrac{25}{16} \end{pmatrix} $$
The vertex of the parabola is the point \( V \left(-\tfrac{3}{8}, -\tfrac{25}{16}\right) \).
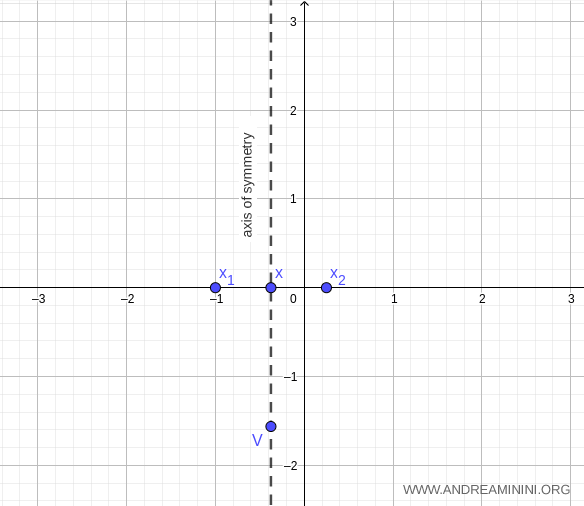
To sketch the curve more precisely, we can calculate additional values of \( y \) for points near the axis of symmetry:
Given the function y = 4x2 + 3x - 1:
$$ \begin{array}{c|lcr} x & y \\ \hline -2 & 9 \\ -1 & 0 \\ 0 & -1 \\ 1 & 6 \end{array} $$
Using these values, we can plot the graph of the parabola:
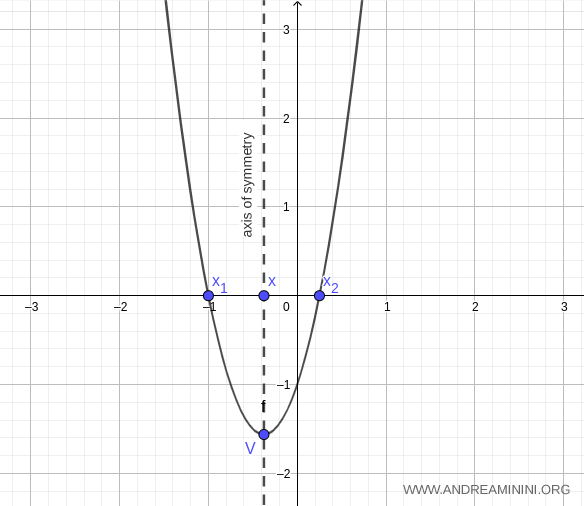
And the process continues in the same way.
