Sign Function
What is the sign function?
- In mathematics, the sign function, written as Sgn(x), is defined by $$ Sgn(x) = \frac{x}{|x|} $$ It returns:
- $f(x) = 1$ if $x > 0$
- $f(x) = -1$ if $x < 0$
It is called the sign function because it outputs the sign of the input value $x$.
Here is the graph of Sgn(x):

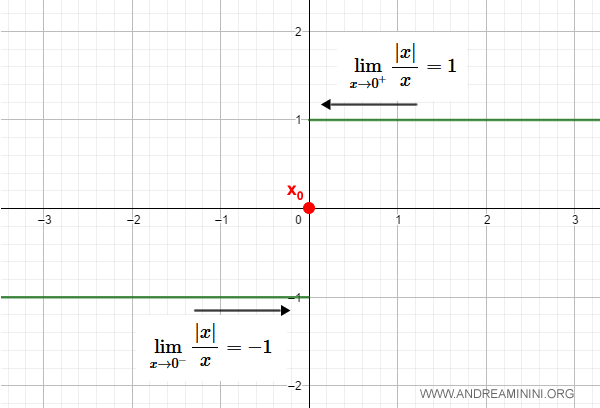
At $x=0$ the function is undefined, since the origin is a point of discontinuity.
The left- and right-hand limits as $x$ approaches zero are not the same:
$$ \lim_{x \rightarrow 0^-} Sgn(x) = -1 $$
$$ \lim_{x \rightarrow 0^+} Sgn(x) = +1 $$
This jump from $-1$ to $+1$ produces a discontinuity at the origin.
From a mathematical standpoint, this is classified as a discontinuity of the first kind. By convention, the value at $x=0$ is often set to $f(0)=0$, which is the midpoint between the two one-sided limits.
And so on.
