Exponential Function
The exponential function is a function of the form $$ y = a^x $$ where the base $a$ is any positive real number ($a > 0$). $$ a \in \mathbb{R}^+ $$
The domain of the exponential function is the entire set of real numbers.
Its range is the set of positive real numbers.
$$ f:\mathbb{R} \;\to\; \mathbb{R}^+ $$
The graph of an exponential function changes depending on the value of the base $a$:
- If the base is greater than one ($a>1$), the graph rises steadily as $x$ increases. In this case, the function is bijective.
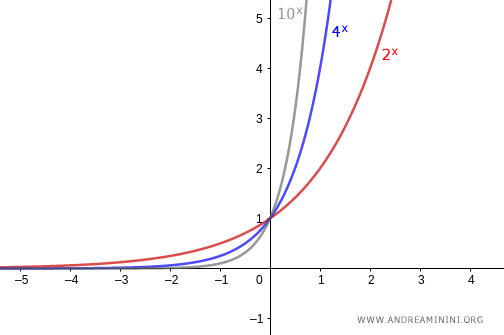
- If the base equals one ($a=1$), the graph is a constant line at $y=1$. This is a non-injective function.
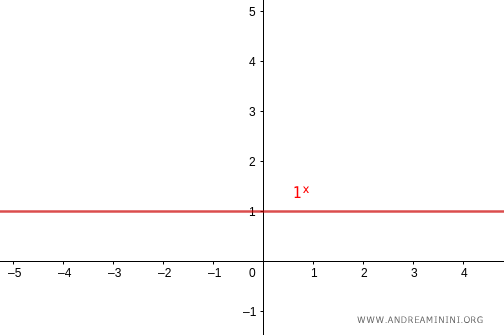
- If the base lies between zero and one ($0<a<1$), the graph falls steadily as $x$ increases. Here too, the function is bijective.
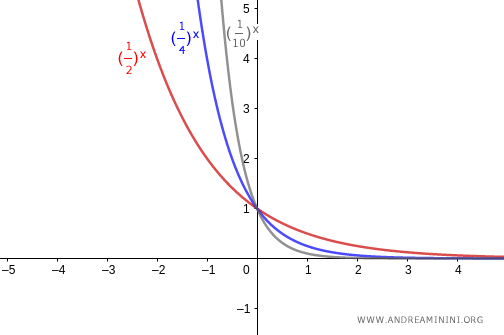
Note. In every case, the graph of an exponential function passes through the point $(0,1)$ on the $y$-axis and never touches the $x$-axis. The function is always positive and is continuous for all real numbers.
And so on.
