Linear Functions
What is a linear function?
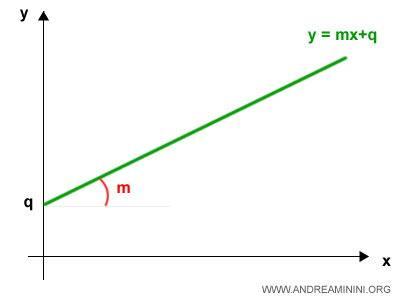
A function is called a linear function (or affine function) when it can be written in the form: $$ y = m \cdot x + q $$ where $ m $ and $ q $ are real numbers.
Linear functions are represented on the Cartesian plane as straight lines.
The parameter $ m $ is commonly referred to as the slope, as it determines the steepness or inclination of the line.
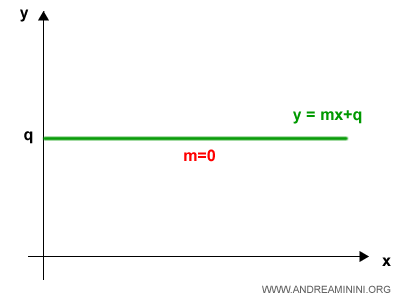
In the special case where $ m = 0 $, the function is known as a constant function, and its graph is a horizontal line parallel to the x-axis.
Note. All linear functions are monotonic - they are either increasing or decreasing. When the slope is nonzero (m ≠ 0), they are also strictly monotonic, meaning they are one-to-one and therefore invertible: $$ y = m x + q $$ $$ x = \frac{y - q}{m} $$
A Practical Example
Consider the following linear function:
$$ f(x) = 2x + 3 $$
The graph of this function is a straight line in the plane.
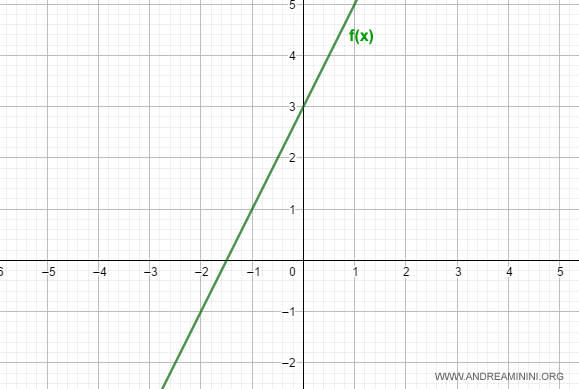
The slope of the line is given by $ m = 2 $, which controls its inclination.
The parameter $ q = 3 $ determines the line’s y-intercept, that is, the point where the line crosses the y-axis.
And so on.
